Define :
When an α-diazo ketone is decomposed thermally photo-chemically or catalytically and converted to ketone by removal of dinitrogen, it is called wolf rearrangement.
The reaction was given by Ludwing Wolf in 1902.
Reaction:
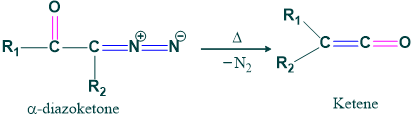
When ketene is formed it acts as an intermediate for forming acid Ester and Amide.

Mechanism of Wolf Rearrangement:
Wolf rearrangement shows a concerted mechanism (single step) or also follows a stepwise mechanism which is as follows;
Concerted Mechanism:
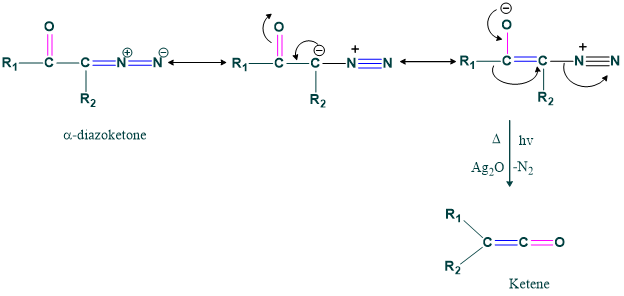 Stepwise Mechanism:
Stepwise Mechanism:
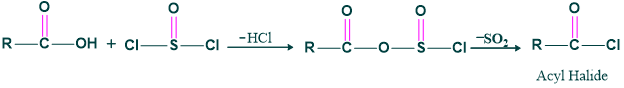
Step(1), Formation of acid halide:
Step(2), Formation of carbene:
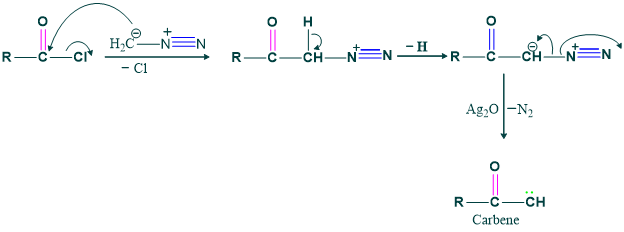
Step(3), Formation of ketene:
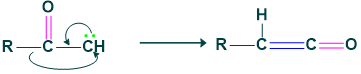
Application of Wolf Rearrangement:
The application of wolf rearrangement is as follows;
- Ring Contraction Reaction
- Higher Homologous
- Formation of oxygen (Photochemical Reaction)
(1)Ring Contraction Reaction:
Wolf rearrangement shows ring contraction reaction as follows;
Mechanism of ring contraction reaction:
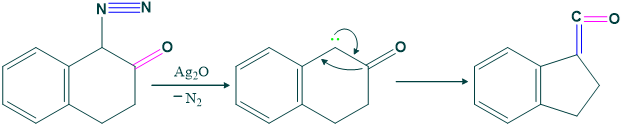
Higher Homologous:
By wolf rearrangement we increase carbon chain length.
Reaction :
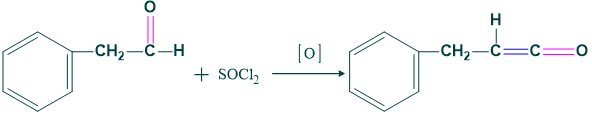
Here we use selective oxidizing agent which is pyridinium chlorochromate and manganese dioxide. Thus;
Mechanism:
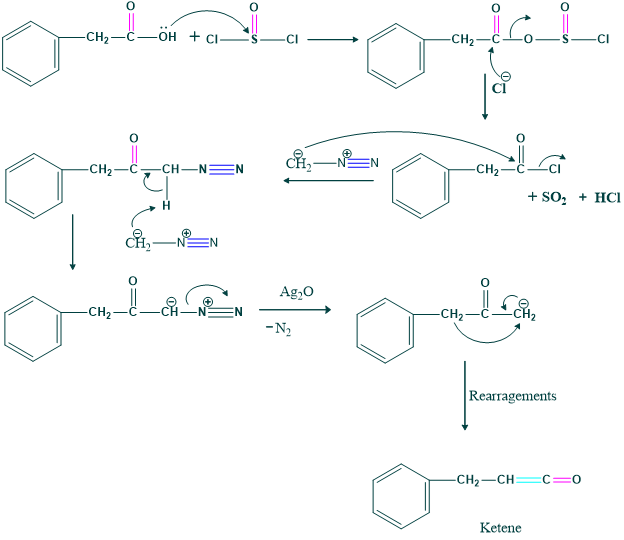
Formation of Oxyrene
It is also known as photochemical reaction .
3 membered ring is relatively highly unstable and break to form carbene and then ketene formation
Mechanism :
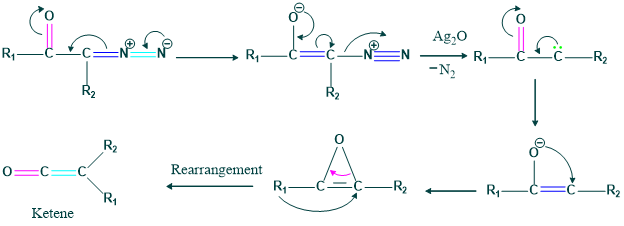 We also form carboxylic acid, ester and amine by different starting material
We also form carboxylic acid, ester and amine by different starting material