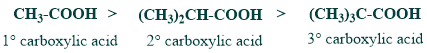What is the steric effect?
- Steric effect is the spatial interaction (non-bonding) due to spatial crowding of bulky groups in a molecule, which affects their stability, properties, and reaction rate.
- Steric effect is one of the factors that affects the stability of a molecule.
- The stability of bulky groups decreases due to the repulsion caused by the steric effect.
- It causes obstruction to the attacking agent, known as steric hindrance.
Applications of steric effect:
1. Stability
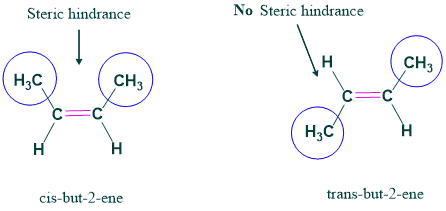
(a) Trans-but-2-ene and cis-but-2-ene
In cis isomers, bulky methyl groups are close by and have steric repulsion, so they are less stable. But in trans, methyl groups being on opposite sides are far away from each other so that there is no steric repulsion and hence more stability.

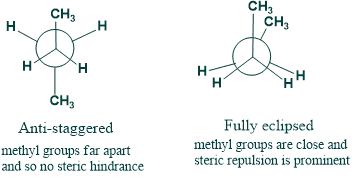
(b) Conformational isomers of butane
- The anti form is most stable since two methyl groups are on opposite sides.
- The repulsion of the bulky groups causes the fully eclipsed form to be the least stable.
2. Basicity of amines
- The unexpectedly lower basicity of tertiary amine is due to steric hindrance to the approach of H⁺ ions and also to the stabilization of the conjugate base through solvation.

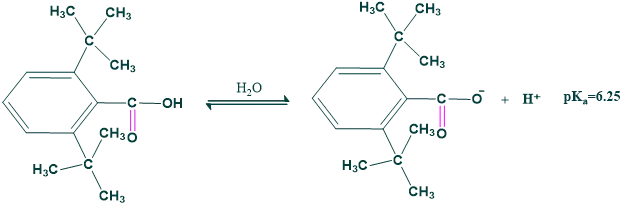
3. Acidity of carboxylic acid
In 2,6-di(t-butyl) benzoic acid, since there is steric hindrance to the stabilization of the carboxylate ion through solvation, it is less acidic than benzoic acid.

4. Reactivity:
(a) SN2 reactivity of alkyl halides
SN2 reactivity of tertiary halides is least because of steric hindrance.
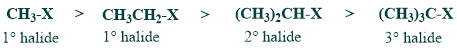
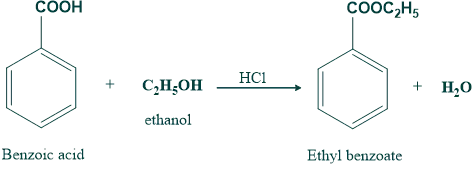
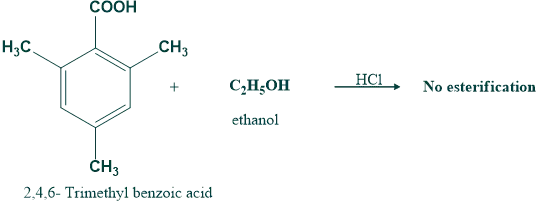
(b) Rate of esterification of carboxylic acid
Steric hindrance to the approach of alcohol to the reaction site on carboxylic acid will lower the rate of esterification.