What is the definition for normality?
The concentration of the solution expressed in a number of equivalents dissolved per liter of solution is known as the normality in chemistry.
Normality is represented by N.
Units of Normality:
Its units are eq/L or meg/L. The latter unit is mostly expressed in medical reporting.
Formula of Normality Chemistry:
These are the formulas to calculate normality:

Steps for calculation:
Here are some steps mentioned that have to be followed to calculate normality:
- In the first step, students should gather information about the equivalent weight of the reacting substance or the solute. Then search the molecular weight and valence through literature.
- In the next step, the number of gram equivalents of solute is calculated.
- Then calculate the volume in liters.
- In the last step, normality is calculated by using the above formula and replacing the values.
How is normality calculated in titration?
- Titration is a technique in which a solution of known concentration and volume is gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the neutralizing reaction occurs.
- By using the given formula, the normality of the acid and base titration is calculated.


Where,
- N1 = Indicates the normality of the Acidic solution
- V1 = Designate the volume of the Acidic solution
- N2 = Indicates the normality of the basic solution
- V3 = Designate the volume of the basic solution
Relationship between Molarity and Normality
Both normality and molarity are necessary terms that play crucial roles in chemistry. They are used for the qualitative measurement of a solute or substance.
Molarity:
It is the number of moles of solute per volume of the solution in liters. It is commonly used for the determination of pH such as dissociation or equilibrium constants, etc.
Formula of Molarity:
Its formula is mentioned below:
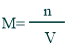
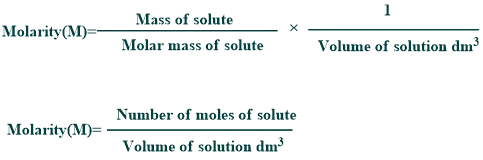
Normality:
It is the number of equivalents dissolved per liter of the solution.
Formula of normality:
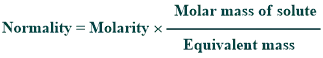
Normality of Bases:
- In the case of bases, the number of H+ are counted that are present in the acid molecule that it can donate.
- The given formula is used to calculate the normality of bases:

Normality of Acids
- In the case of acids, the number of OH⁻ ions present in the base molecule that it can donate is counted.
- The given formula is used to calculate the normality of acids:

Conversion of molarity to normality:
Molarity can be converted into normality by using the given formula:

Normality of Acids:
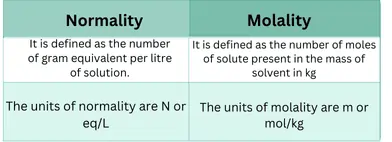
Describe the difference between normality and molarity:
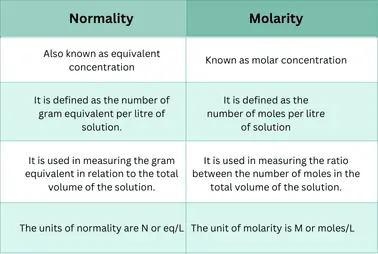
What is the difference between normality and molality?