What is Molality?
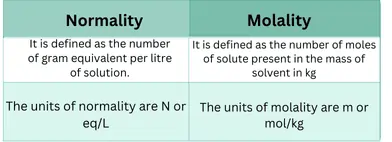
The molality of a solution is the number of moles of solutes per kilogram of solvent.
- It is designated by ‘m’.
Molality Formula
Its formula is given below:
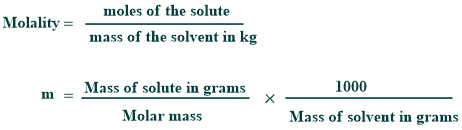
How to find molality:
It can be calculated by using its formula.
For Example,
Molality of pure water
As it is known, the density of pure water is 1 kg per liter, and its molar mass is 18 g per mole. Therefore,
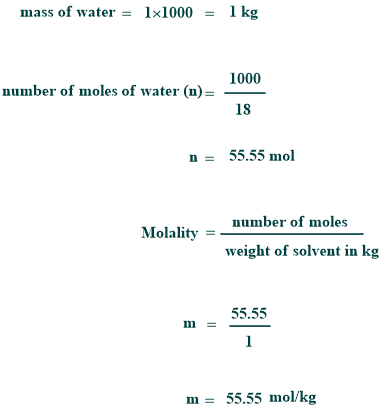
However, the molality of pure water is 55.55 molal.
If a solution containing 5.3 grams of anhydrous Na₂CO₃ in 200 g of water, then its molality can be calculated as follows:
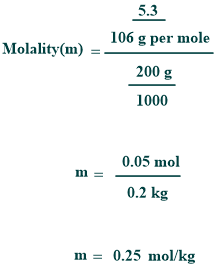
As a result, the molality of the anhydrous sodium carbonate solution is 0.25 molal.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using molality?
Advantage
- It does not depend upon the temperature, because when substances are heated or cooled, their masses are not changed.
Disadvantage
- It is the amount of solution that is measured by mass instead of volume, and the density of the solution must be known to convert molality into molarity.
Relationship between molality and molarity
Their relationship is given below:
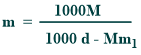
Where,
d = the density (g/ml)
m₁ = the molar mass of the solute
M=molarity
m=molality
Frequently Asked Question:
Describe the difference between molarity and molality?

What is the application of molality in real life?
- Boiling point is determined by using molality.
- It is used to measure the melting point.
- For colligative properties like boiling point elevation and freezing point depression.
What are the factors affecting molality?
Molality is determined by the mass of the solute and the solvent. It is temperature-independent.