What is glycerin?
Glycerin is a type of carbohydrate called a sugar alcohol, or polyol. Glycerin, also known as glycerol, is a natural compound derived from vegetable oils or animal fats. It’s a clear, colorless, odorless, and syrupy liquid with a sweet taste.
Glycerin contains slightly more calories per gram than sugar and is 60–75% as sweet.
Glycerine is also a significant component of triglycerides (fat found naturally in your body). Pure glycerin looks like a thick and transparent liquid
Glycerin is a humectant, a type of moisturizing agent that pulls water into the outer layer of your skin from deeper levels of your skin and the air.
In skin care products, glycerin is commonly used with occlusives, another type of moisturizing agent, to trap the moisture it draws into the skin. According to a 2016 study, glycerin is “the most effective humectant” available to increase hydration on the top layer of your skin, in comparison with numerous others, including urea, alpha hydroxy acids, like lactic acid and glycolic acid, hyaluronic acid, propylene glycol and butylene glycol, sorbitol
Chemistry of Glycerin:
In chemistry a molecular formula indicates every single atom and its numbers in a chemical compound. Hence, the molecular formula C₃H₈O₃ simply says that there are three carbon (C) atoms, eight hydrogen (H) atoms, and three oxygen (O) atoms in this compound.
This molecular formula on its own does not indicate how the atoms interact with each other or whether bonding occurs between them.
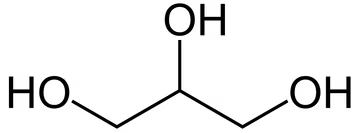
Trihydric Alcohol
The molecular formula for glycerine can also be presented differently; C₃H₅(OH)₃ is also a molecular formula for glycerine used in chemistry. If we take a closer look at this formula, we see that three oxygen (O) atoms and three hydrogen (H) atoms are bonded, namely in the OH group. This hydroxyl group (-OH) is the functional group of alcohols. Glycerine (chemically correct name “glycerol” or “propanetriol”) is called a trihydric alcohol, as it occurs exactly three times in the structural formula C₃H₈O₃. Incidentally, glycerol is the right name because in chemistry the suffix -ol is correct for alcohol. Propane-1,2,3-triol is the IUPAC name for glycerine, the simplest and, at the same time, most important trihydric alcohol. This substance is very common in nature

Vegetable glycerin:
Vegetable glycerine, also known as glycerol, is a transparent liquid usually made from soybean, coconut, or palm oils. It is odorless and has a moderate, sweet taste with a consistency that resembles syrup.
Properties of Glycerine – C3H8O3:
| C3H8O3 | Glycerin |
| Molecular weight/ Molar mass | 92.09 g/mol |
| Density | 1.261 g/cm³ |
| Boiling point | 290 °C |
| Melting point | Molecular weight/molar mass |
Glycerine consumption:
When we consume glycerin, it is readily and completely absorbed in the small intestine. Like other sugar alcohols (with the exception of erythritol), glycerin contains calories in the form of carbohydrates. Yet despite its being a carbohydrate source, glycerin does not significantly promote insulin secretion when it’s consumed, which helps keep the body’s blood glucose levels lower than the levels produced by eating other types of carbohydrates, including sugars.
Recommended intake:
Glycerin is not an essential part of a balanced diet, but consuming it (even in high amounts) has not been shown to be detrimental to human health. Therefore, no acceptable daily intake level has been established.
Consuming large doses of glycerin at one time may produce mild laxative effects, headache, thirst, nausea, or hyperglycemia, but such quantities are not found in individual foods or a typical diet.
Unlike other polyols, glycerin is not considered necessary to exclude as part of a low Fermentable Oligosaccharides Disaccharides Monosaccharides And Polyols (FODMAP) diet because it is completely absorbed in the small intestine and does not reach the large intestine.
Food sources of glycerin:
Because of its versatile attributes as a moisture retainer, preservative, sweetener, and thickener, glycerin is used in a wide variety of foods and beverages, including nutrition and energy bars, various drinks, cake icings, soft candies, chewing gum, condiments, diet foods, dried fruits and vegetables, marshmallows, soups, spices, and seasonings. Glycerin is also naturally found in fermented foods and beverages such as beer, honey, vinegar, wine, and wine vinegar.
Glycerol, is a carbohydrate added to skincare, medications, and foods. Glycerin can help sweeten, preserve, thicken, and improve the texture of foods, supplements, and medication. Glycerin also has water-retaining properties that can help moisturize the skin and eyes and relieve constipation.
Dairy and Protein Foods:
Dairy products, including cheese, yogurt, and powdered milk or cream, are among the potential sources of glycerin. You may also find glycerin in condensed milk, whey products, pudding, clotted cream, and dairy-based drinks. Processed meat and poultry, soybean products, processed seafood, dried eggs, canned eggs, and egg-based desserts can contain this additive as well. Check the ingredients list to verify whether individual products contain glycerin.
Processed Vegetables and Fruits:
Vegetables and fruits generally don’t contain glycerin unless they’re processed. Some examples of vegetables that could have glycerin include dried vegetables, canned vegetables, processed fruit, precooked vegetables and sauces containing vegetables. If you’d like to avoid glycerin, opt for fresh fruits and vegetables or those frozen without any added sauces.
Grains and Baked Goods:
Precooked pasta, rolled oats, breakfast cereals, rice or tapioca pudding, breading or batters, precooked rice products, and baked goods are all potential sources of glycerin. The less processed a grain-based food is, the less likely it is to contain glycerin. Baking goods and cooking grains yourself will help you limit your glycerin intake.
Other Foods:
Many other foods can also be sources of glycerin. Some potential beverage sources of glycerin include alcoholic beverages, cider, and flavored beverages made with water. The little extras you add to your food, such as sauces, vinegar, mustard, condiments, tabletop sweeteners, butter and similar spreads, and nut butters, may contain glycerine, and so can candies, soups, and edible ices. Foods with added sweeteners sometimes contain glycerin because of the sweet taste it imparts.
Glycerin benefits for skin:
Moisturizes your skin
Glycerin gives the skin a refreshed look and aids in moisturization by drawing water from the deeper levels of the skin towards the surface layer of the skin and locking it in. That way, the skin obtains the necessary hydration to give it a fresher, healthier, and smoother look.

During the winter, the dryness and low humidity in the air can easily cause the skin to dry out, making the skin less elastic and more prone to cracking. Glycerine helps protect your skin from these harsh external factors, leaving it moisturized with a soft feel.
2. Protects your skin
Glycerin has antimicrobial properties, such as bacteria and fungi, which protect the skin from harmful microorganisms that can cause many undesirable conditions and health problems.
3. Keeps your skin young
Glycerine draws moisture from the surrounding environment (Think of glycerine as a sponge that absorbs water!). This water retention increases the skin’s elasticity and hydration. It also reduces the appearance of wrinkles, giving you smoother and younger-looking skin.

4. Safe moisturizer for all skin types
Some compounds used in skin care products may irritate people with varying types of skin. However, glycerin has effective moisturizing properties while being gentle on the skin and does not cause irritation or clog pores. Glycerin is even suitable for children and is used in various baby products.
5. Helps damaged skin and useful in healing wounds
Glycerin has skin-repairing and antimicrobial properties; therefore, it promotes the health of damaged skin and protects it from bacteria and other harmful microorganisms. In addition to its effectiveness in giving the skin moisture and helping to increase its elasticity, glycerin also improves the skin’s natural defensive barrier.
The Benefits of Glycerine for Hair
Glycerine isn’t just an ordinary hair care ingredient. It’s a powerhouse of moisture that transforms your locks. Here are some of the fantastic ways glycerine can benefit your hair!
Deeply Moisturizes and Hydrates Hair:
One of the standout qualities of glycerin is its exceptional moisture attraction and retention capabilities. In fact, glycerin is one of the best humectants for hair, alongside honey.
Glycerin’s humectant properties allow it to attract water molecules from the environment and lock them into your hair strands. This means that even on the driest of days, glycerin-infused hair products can help keep your hair hydrated, preventing it from becoming dull, brittle, and prone to breakage.
Softening Properties
Glycerin is the secret to soft, silky hair! It helps to smooth the hair cuticle, leaving it softer and more manageable. Whether you have coarse curls or fine locks, glycerin can help you achieve the touchable, silky-smooth texture you’ve always dreamed of.
Scalp Health
Healthy hair starts at the roots, and glycerin doesn’t leave your scalp out of the equation. It can assist in maintaining healthy hair follicles by preventing excessive dryness and flakiness. A well-moisturized scalp promotes healthier hair growth and reduces itchiness and irritation.
Thanks to its hydrating and moisture retention benefits, scalp treatments that contain glycerin can also help to balance the scalp microbiome and prevent excessive oil production. The infusion of moisture that glycerin provides helps to regulate oil production in the
Frizz Control
Are frizz and flyaways your daily nemesis? Glycerin can come to the rescue! By maintaining your hair’s natural moisture balance, it helps reduce frizz and keeps those unruly locks in check. This means you can step out on humid days with confidence, knowing that your hair will stay smoother for longer.
Improved Elasticity and Reduced Split Ends
Glycerin helps your hair maintain its elasticity, which is essential for preventing breakage. When your hair has good elasticity, it can stretch and bounce back without snapping. This is especially beneficial for those with curly hair, as it helps maintain curl definition and bounce.
Dry, damaged hair is also prone to split ends. Glycerin can help to reduce split ends by strengthening and moisturizing the hair. This also helps to reduce breakage and prevent existing split ends from traveling further up the hair shaft.
Overall Hair Health
Ultimately, glycerin contributes to the overall health of your hair. When your locks are adequately moisturized, they’re less prone to damage, whether from heat styling, environmental factors, or daily wear and tear. Glycerin not only enhances the appearance of your hair but also strengthens it from within.

Glycerin Benefits for Different Hair Types:
Glycerin is extremely versatile and can work wonders for a wide range of different hair types. It can be especially beneficial for thick, coarse, dry, or dehydrated hair types. Let’s take a closer look at how glycerin can be tailored to suit your specific hair type.
Straight Hair:
If you’re blessed with straight hair, glycerin is ideal for adding moisture and shine without weighing your hair down. Look for lightweight hair products that contain glycerin to maintain that sleek and polished look.
Wavy Hair
Wavy hair falls somewhere in between straight and curly, leaving it prone to dryness and frizz. Glycerin-infused products can help you achieve that effortlessly tousled look while adding hydration and keeping frizz at bay.
Curly Hair
Naturally curly hair thrives on moisture, making glycerin a curly-haired gal’s best friend! It helps to define curls, reduce frizz, and keep your locks bouncy and hydrated. Look for deep-conditioning hair masks with glycerin as a key ingredient to enhance your natural curl pattern.
Coily Hair
Coily hair can be prone to dryness and shrinkage, but glycerin can help combat both. Opt for deep conditioning treatments, like our Honey Infused Hair Mask, that contain glycerin and other natural ingredients to nourish and elongate your curls. Glycerin’s moisture-retaining properties work wonders for defining curls, reducing frizz, and maintaining the health of coily hair.
How to Use Glycerin for Hair
Before you introduce glycerin into your haircare routine, there are a few key factors to consider to make the most of this magical ingredient. Here are some tips to keep in mind.
Weather Considerations
Glycerin’s moisture-attracting superpower can be a double-edged sword in extremely hot and humid environments. When it’s very humid, glycerin can draw in excess moisture from the air, potentially causing your hair to swell and frizz. If this is a problem for you, consider using glycerin more sparingly in the summer months to avoid overly soft or limp hair.
However, in the colder, drier months of winter, glycerin is ideal for keeping your hair soft and hydrated. Feel free to incorporate glycerin into your hair care routine more freely for added hydration and shine.
Hair Porosity
Hair porosity refers to your hair’s ability to absorb and retain moisture. Understanding how glycerin interacts with your hair’s porosity can help you use it more effectively.
- Low Porosity: If you have low-porosity hair, consider using glycerin more sparingly. Your hair doesn’t readily absorb moisture, so too much glycerin may weigh it down. Opt for products with glycerin lower on the ingredient list.
- Normal Porosity: Normal porosity hair responds well to glycerin. You can enjoy its benefits without any major concerns.
- High Porosity: High porosity hair can benefit greatly from glycerin, as it helps to retain much-needed moisture. However, remember to apply it more sparingly in extremely humid conditions, as your hair may absorb too much moisture and become more prone to frizz.
Layering Products
Layering products is a great way to make the most of glycerin’s beneficial effects, especially in challenging weather conditions. For example, follow our glycerin-rich Wash & Go Combo with our glycerin-free Honey-Infused Hair Repair Serum. This layered approach can help you achieve the right balance of moisture and control.

Protective Styling
Consider using glycerin-rich products when creating protective hairstyles. Glycerin can help maintain moisture levels in your hair while it’s tucked away in braids, buns, or other protective hairstyles, reducing the risk of breakage and leaving the hair moisturized and shiny.
Shampoo and Condition
Begin your glycerin-infused routine in the shower. Use Honey-Infused Hair Wash to cleanse your hair without stripping away the natural oils. Follow with our Honey-Infused Hair Mask and Honey-Infused Conditioner to seal the cuticles and lock in moisture.
Wrapping Up
Whether you have straight, wavy, curly, or coily locks, glycerin is a versatile ally that adapts to your hair’s unique needs. With our honey-infused hair care products, plus a little thoughtful application, you’ll be well on your way to experiencing the transformational power of glycerin.
Embrace this moisture-locking marvel, make it part of your daily routine, and let glycerin help you unleash your hair’s full potential. Say goodbye to dryness, frizz, and lackluster locks, and hello to hair that radiates health and vitality!
Uses of Glycerin:
The primary application of glycerin is in the food and beverage industry, where it is employed as a humectant, sweetener, and as a solvent. Glycerin is also used as a preservative for the storage of food items. Some important uses of glycerin have been listed below.
- Glycerin is used in the food industry as a sweetener and preservative
- It is also used in liqueurs as a thickening agent
- It is not uncommon for glycerin to be used as a filler in low-fat food items such as cookies
- Another important use of glycerin in the medical and pharmaceutical industries is as a lubricant and humectant
- Glycerin is used in the treatment of severely increased eye pressure
- Owing to its moisturizing properties, glycerin is used in many skin-care products that help prevent dry skin
- C3H8O3 is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the preparation of cough syrups
- Glycerin is a vital component of many skincare products. Furthermore, this compound is also used in the production of toothpaste
- Another key application of glycerin is its use in the production of electronic cigarette liquid
- It is used in explosives such as dynamite
- C3H8O3 is used as a fill to damp the vibrations in pressure gauges
- Glycerin is used in film industries to avoid the quick drying of wet areas.
Glycerin can be used as a moisturiser, solvent, and as a sweetener in food and beverages. This compound can also help preserve certain foods. Glycerin is also known to be used in commercially packaged low-fat foods (such as cookies) as a filler. Furthermore, this compound is also known to be used in liqueurs as a thickening agent. In order to protect some forms of plant leaves, glycerol and water can be used.
Glycerin has approximately 27 kilocalories per teaspoon as a sugar substitute (sugar is known to have 20) and is 60 per cent as sweet as sucrose. Therefore, glycerin is a great sugar substitute. Furthermore, this compound does not nourish the plaque-forming bacteria that produce dental cavities.
Glycerin is moderately antimicrobial and antiviral and can therefore be used for wound treatment. An 85 percent glycerin solution is known to show bactericidal and antiviral effects, and glycerin-treated wounds generally display decreased inflammation after an approximate timeframe of 2 hours.Because of this, it is commonly used in wound care materials, including hydrogel sheets based on glycerin for burns and other wound care products. With the exception of third-degree burns, glycerin is licenced for all forms of wound treatment and is used to package the donor skin that is used in skin grafts. It can also be noted that there is no authorised topical therapy for third-degree burns and this restriction is also not limited to glycerin.
Best glycerin for skin:
While browsing the internet or the aisles, you may be overwhelmed by the number of glycerin products to choose from. While certain brands may seem trendier than others, it’s important to get the kind that reacts best with your particular skin type. Keep in mind that it might not be one of the popular brands. When choosing the best glycerin for your skin, consider talking with a dermatologist first to learn more about your specific skin type and what product would be best.One option also available is glycerin soap, which is generally recommended for people with sensitive skin.
What are the uses of glycerin?
Applications of glycerin: This compound is used as a moisturizer to treat or avoid dry, raw, scaly, itchy skin and mild skin irritations (e.g., diaper rash, skin burns from radiation therapy). Emollients are substances that relax and humidify the skin, and reduce scratching and flaking.
What does glycerin do to the skin?
Applying glycerine to the skin retains moisture in the skin and gives it a safe, youthful glow. Glycerine helps to reduce the emergence of wrinkles by attracting moisture to the top layer of skin and leaves the skin looking soft and smooth. Additionally, glycerine increases skin function to delay ageing.
Is glycerin safe to eat?
Typically, glycerin is used as a sweetener and preservative in food items. This compound is quite safe for consumption. In fact, glycerol can be classified as a caloric macronutrient. However, it is important to note that some individuals may be allergic to glycerin. This compound may be toxic to such people.
How can glycerol be produced?
Generally, glycerine is obtained from animal and plant sources. It is known to naturally occur in the form of triglycerides, which are esters of glycerol featuring carboxylic acids with long chains. The preparation of glycerin can also involve the use of propylene as feedstock. One of the most important uses of glycerin is in the food and beverage industry, where it serves as a humectant.
Is Glycerin Halal?
The halal status of glycerin depends on its source and method of extraction. For glycerin to be halal, it should:
Be derived from plant sources. This includes glycerin obtained from vegetable oils or other plant-based materials.
Be produced synthetically in laboratories, as that does not involve the integration of any animal-derived ingredients
Is glycerin good for your skin?
Glycerin’s appearance in skin care products seems to be warranted, as there are a number of benefits it brings to your skin.
Are there side effects to using glycerin?
Although there don’t appear to be many reported side effects, glycerin is a natural product, so there’s always potential for an allergic reaction.
If you experience redness, itching, or rash, stop using the product immediately. Look for an alternate product that doesn’t contain glycerin, and be sure to read the labels carefully.
How to use glycerin on the face?
First, rinse your face with cold water.
Put glycerin on a cotton pad or tissue and gently blot your face.
Let the glycerin absorb into your skin for a few minutes.
Gently rinse off the glycerin with water.
Warning:
It’s very important to dilute glycerin before using it directly. Applying diluted glycerin to the face is an easy process, and typically very safe. But if it’s not diluted, it can badly irritate your skin — or worse.
If you choose to use diluted glycerin, make sure you don’t get it in your eyes and mouth.