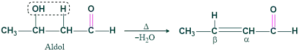
Carbonyl compounds having α-H atom undergo self-condensation reaction on warming with dilute acid or dilute base and give β-hydroxy carbonyl compound [Aldol]-which on heating lose water molecule and give α,β unsaturated carbonyl compound. This phenomenon is called the aldol condensation reaction.
Reactant: Carbonyl compound having α-H
Product: β hydroxy carbonyl [Aldol] α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound
Catalyst: Acid/Base
Reaction of aldol condensation:
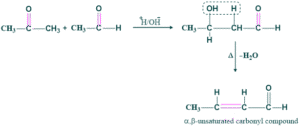
Aldol addition is the addition of of alcoholic group in contrast with reactant because in aldol, “Ald”, means “aldehyde” and “ol” means alcohol, a combination of two words,
While aldol condensation is the removal of water from aldol addition product on heating gives α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound
Reaction Mechanism of Aldol Condensation:
Aldol condensation is promoted by two types of mechanisms.
(1)Base catalyzed mechanism
(2) Acid-catalyzed mechanism
Base Catalysed Mechanism
According to the Lowery-Bronsted concept
Step(01) Formation enolate ion:
In the the first step, the base attacks the carbonyl compound and extracts hydrogen ions from it and from the enolate ion which acts as a nucleophile. In this step, we use a hydrogen oxide base. Because oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons hydrogen oxide is an electron-rich species and attaches to acidic hydrogen for water formation.

Step(02) nucleophilic addition :
In the second step, nucleophilic addition takes place, and enolate ions act as nucleophiles. This nucleophile attacks on the carbonyl compound and form alkoxide ion. Alkoxide ion is a conjugated base of alcohol.

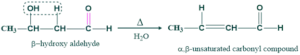
Step(03)
In this step, the alkoxide ion deprotonates a water molecule and forms a hydroxide ion i.e. β-hydroxy aldehyde or aldol product.
Deprotonation of water
![]()
Here alkoxide ion is protonated by water molecule.
Step(04) dehydration:
In this step, the removal of water takes place on heating giving aldol condensation i.e. α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Acid Catalysed Mechanism:
In the acid-catalyzed mechanism, we used acid.
Step(01) enol formation:
In this step, the carbonyl compound of aldehyde or ketone contains an oxygen atom. This oxygen atom contains two lone pairs of electrons. This lone pair of oxygen attacks on acidic hydrogen and form enol.
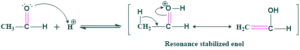
Step(02) nucleophilic addition:
In this step, enol acts as a nucleophile and attacks another resonance form of enol which is less stable.
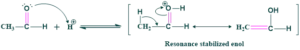
Step(03) dehydration:
Water removal takes place on heating giving α,β- unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Types of aldol condensation Reaction:
Two types of aldol condensation are discussed below.
(01) simple aldol condensation
(02) cross aldol condensation
Simple Aldol Condensation Reaction:
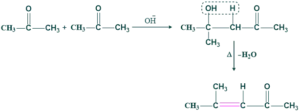
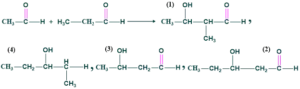
The simple aldol condensation reaction that takes place between two same carbonyl compounds and gives only one product is called simple aldol condensation.
The same carbonyl compound mean
- Both aldehydes have α- H gives one product only
- OR both ketones having α-H also give one product only
Examples:
Simple aldol condensation of aldehyde:
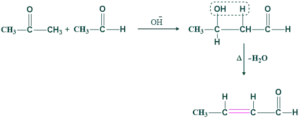
Simple aldol condensation of ketone:
Cross Aldol condensation :
The condensation that takes place between two different carbonyl compounds (either aldehyde or ketone) gives two types of product.
- If both aldehyde or ketone have an α-H give four different product
- If only one carbonyl compound has an α-H gives two different product
This is called cross aldol condensation.
Examples:
We use two different aldehydes both having α-H give four products.
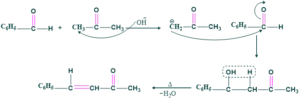
What is Claisen’s Schmidt Reaction?
Reaction in between aromatic aldehyde and ketone in the presence of base gives aldol (α,β-hydroxy ketone) which on heating yields α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound. This overall reaction is called the Schmidt reaction.
Directed Aldol Condensation:
OH is the typical base used in aldol condensation reaction but instead of OH base, we use another base which is LDA ( Lithium di-isopropyl amide).
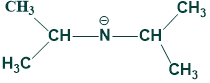
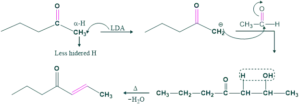
This base has a bulky group, so it directly attacks less hindered H-atom and gives a product. This is called directed aldol condensation.
Examples No.1
Examples No.2
![]()
Cyclization of Aldol Condensation:
Cyclization of aldol condensation is also called intramolecular aldol condensation
Examples No.1
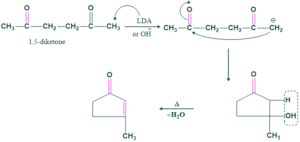
If OH is used, then it attacks on more hindered α-H and gives a four-membered ring product which is sterically unstable. So to yield a stable product we use base LDA. It attacks less hindered α-H and gives a five-membered ring product that is stable.
Examples No.2
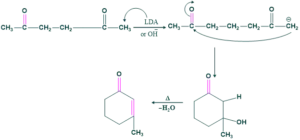
Here OH is also used, OH gives either a five-membered or six-membered ring, so both are stable products. In this case, we also used a typical base which is OH instead of LDA.
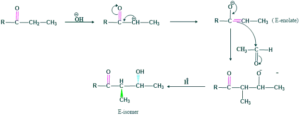
Diastereoselectivity of Aldol Reaction:
Aldol reaction gives two diastereoselective products.
- Z-enolate
- E-enolate
Z-enolate:
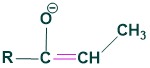
- this is called zenolate
- This enolate is also called thermodynamic enolate
- This is more stable and gives syn diastereomer which is a major product

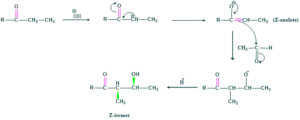
E-enolate:
- E-enolate is kinetic enolate
- E-enolate is less stable