What is the resonance effect?
- The decrease in electron density at one position accompanied by a corresponding increase at another position by the movement of pi electrons is called the resonance effect.
- The resonance effect is also known as a mesomeric effect.
- The distribution of electron density depends on the resonance in a system. The distribution of electron density is different in resonant systems than the non-resonant systems.
- For example, Ammonia has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, but does not have resonance.
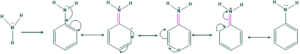
- But if one of the hydrogen atoms of the ammonia molecule is replaced by a benzene ring, then the electron pairs on the nitrogen atom show delocalization on the ring, as a result the electron density is decreased on the nitrogen atom and the electron density is increased on the benzene ring as shown below:

Thus, it can be said that the -NH2 group in aniline gives electrons to the ring by the resonance effect.
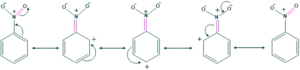
- In a similar fashion, the –NO2 group in nitrobenzene withdraws electrons from the ring by a similar effect.
Types of resonance effect:
There are two types of resonance effects which are given below:
- Positive resonance effect
- Negative resonance effect
Positive resonance effect:
- The positive resonance effect takes place when electrons or pi electrons are donated from a specific group to a conjugate system, which increases the system’s electron density.
- This occurs when the groups are delocalized and donate electrons to the other molecules.
- A group which contains either a single pair of electrons or a negative charge , shows the positive resonance effect..
- It is also called as positive mesomeric effect.
- It is denoted by +R and +M.
- The positive effect can be seen in the following groups in this specific order:
![]()
Negative resonance effect:
- The negative resonance effect takes place when the groups withdraw electrons from other molecules by the process of delocalization.
- It decreases the molecular electron density.
- A group which contains either a positive charge or vacant orbital ,shows the negative resonance effect..
- It is also known as the negative mesomeric effect.
- It is denoted by -R and -M.
- The groups which are given below exhibits the negative resonance effect in this order:
![]()
![]()