The Mole Definition in Chemistry
The mole definition is the amount of a substance that includes the same number of elementary particles (ions, molecules, or atoms) as a carbon atom.
OR
A mole in chemistry is defined as the amount of a substance that contains precisely 6.02214076 x 1023 ‘elementary entities’ of the supplied substance.
The Avogadro constant, or 6.02214076 x 1023, is commonly abbreviated as ‘NA‘. Atoms, molecules, monoatomic/polyatomic ions, and other particles (such as electrons) are examples of elementary things that can be represented using moles.
For example:
One mole of pure carbon-12 (12C) has a mass of exactly 12 grams and contains 6.02214076 x 1023 (NA) 12C atoms.
How to calculate moles in chemistry?
The formula for calculating the number of moles of a substance in a pure sample is as follows:

Where:
- n represents the number of moles of the substance.
- N designated to the total number of elementary entities in the sample
- NA represents the Avogadro constant
The number of moles in a molecule does not always equal the number of moles in its constituent constituents. For example, a mole of water consists of 1 NA number of H₂O molecules. So, each water molecule is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Therefore, one mole of H₂O contains two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen.
Atomic mass
The atomic mass of the element expressed in grams is called one gram atom or mole of a substance. It accounts for the abundance of the element’s various isotopes and calculates the average mass of one atom.
For example,
Carbon has an atomic mass of 12.011 units because carbon compounds usually contain 98.89% carbon-12, 1.11% carbon-13, and trace amounts of carbon-14. So, these isotopes contain different atomic masses.
A carbon-12 atom has an atomic mass of 12, whereas a carbon-13 atom has an atomic mass of 13. An element’s atomic mass is approximately equal to the total of its protons and neutrons.
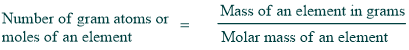
1 gram atom of hydrogen atom = 1.008 g
1 gram atom of uranium = 238.0 g
Molecular mass
An element’s molecular mass is equal to the sum of its constituent elements’ atomic masses. The molecular mass of an element is also shown in terms of atomic mass units. As a result, the molecular mass of water is equal to the sum of its constituent atomic masses, which are hydrogen and oxygen respectively.
The atomic mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.00794 amu, and the atomic mass of oxygen is 15.9994. H₂O has a molecular mass of 18.0154 amu because it is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen.
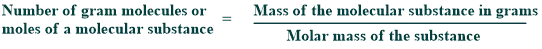
1 gram molecule of water = 18.0 g
1 gram molecule of H₂SO₄ = 98 g
1 gram molecule of sucrose = 342.0 g
Formula mass
The formula unit mass of an ionic compound is determined in terms of grams and is called the gram formula of the substance.
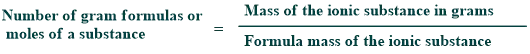
1 gram formula of NaCl = 58.50 g
1 gram formula of Na₂CO₃ = 106 g
Ionic mass
The ionic mass of an ionic species expressed in grams is called one gram ion or mole of ions.
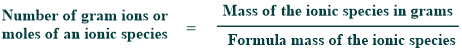
1 g ion of OH– = 17g
1 g ion of SO₄2- = 96g
1 g ion of CO₃2- = 60g
Molar mass
The molar mass of a substance is the entire mass of one mole. It is usually shown in terms of ‘grams per mole’ (g/mol). So, the SI unit for this quantity is kg/mol. Molar mass is expressed by the given formula:
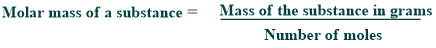
A substance’s molar mass is calculated by dividing its mass in grams by its number of moles.
For example, water has a molar mass of approximately 18.015 g/mol, which is the mass of the number of water molecules.
Frequently Asked Question
What is the Avogadro’s Number?
- Avogadro’s number is the number of atoms, molecules, and ions that are expressed in terms of one gram atom of an element,one gram molecule of a compound, and one gram ion of a substance, respectively.
1.008g of hydrogen atom = 1 mole of hydrogen = 6.02 x 1023 atoms of H
18g of H2 O = 1 mole of water = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of water
96g of SO4 2- = 1 mole of SO4 2- = 6.02 x 1023 ions of SO4 2-
- 6.02×1023 is the number of atoms in one mole of the element.
- There are three relationships between amounts of substances in case of their atomic masses and the number of particles. These relationships are given below:
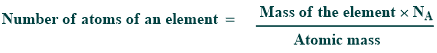

What is the molar volume?
One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure occupies a volume of 22.414 dm3. This volume of 22.414 dm3 is called molar volume and it is true only when the gas is ideal.
2.016 g of H2 molecule =1 mole of H2 = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of H2 = 22.414 dm3 of H2 at S.T.P.
16g of CH4 molecule = 1 mole of CH4 = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of CH4 = 22.414 dm3 of CH4 at S.T.P.
How to find moles in chemistry?
The number of moles of any given substance can be determined by dividing its mass by its molecular weight.

What is the basic concept of a mole?
A mole is defined as the amount of a compound that contains 6.02214076 x 1023 ‘elementary entities’ of that compound.
Part 1:
Part 2: