[ez-toc]
What are steroids?
- Steroids are a class of natural products which are distributed in animals and plants.
- Steroids are named after steroid cholesterol which was first discovered in gall stones from Ancient Greek chole means ‘bile’ and stereos means ‘solid’.
- Sterols, cholesterols, vitamin D, bile acids, sex hormones, adrenal cortex hormones, some carcinogenic hydrocarbons, and some sapogenins etc all are steroids.
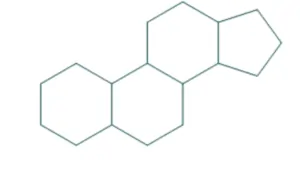
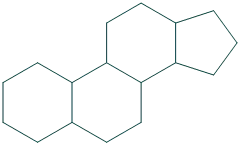
- These are organic compounds primarily consist of seventeen carbon atoms containing four fused rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration, three rings are six carbon membered but one ring is five carbon membered.
- Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene also known as gonane is a nucleus of all steroids.
 Classification of steroids:
Classification of steroids:
Steroids are classified on the basis of variations in their functional groups attached with their core structure:
1. Sterol:
These core structure of steroid ( C-17) with the aliphatic side chain and one or more hydroxyl groups attached with them, these are also called steroid alcohols.
Phytosterols
- Phytosterols are natural products occur in plants that can help in lowering the cholesterol level to avoid health risks i.e. heart attack and stroke. They help to avoid obesity, diabetes and cancer.
- Some sources of phytosterols are unrefined vegetable oils, seeds, cereals, nuts and legumes.
- The widely present plant sterols are beta- sitosterol, campesterol and stigmasterol. The daily intake of these phytosterol is ranging from 150 to 400 mg per day.
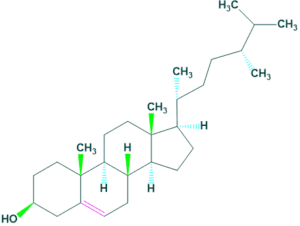
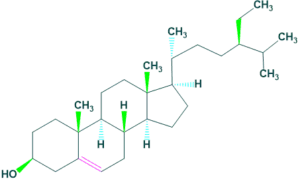
 Mycosterols
Mycosterols
- Mycosterols are natural products occur in fungi. It is present in the cell membrane of fungi which play same function as cholesterol in animals.
- The most common mycosterol is ergosterol which is occur in many sources but is abundant in mushrooms.
- The content of ergosterol are 3.52 mg/g and 0.43 mg/g in button mushrooms and morel mushrooms respectively.
 Zoosterols
Zoosterols
- Zoosterols are natural products occur in animals. It play important role in the serum as a cholesterol precursor and is photochemically converted to vitamin D3 in the skin, so function as provitamin-D3.
- Provitamin D3 present in humans skin play role in the manufacturing of vitamin D3 ( cholecalciferol).
- Most of common examples of cholesterol and Coprostanol.
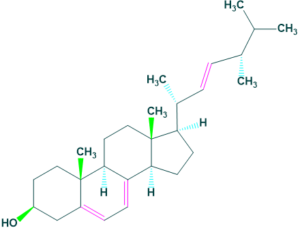
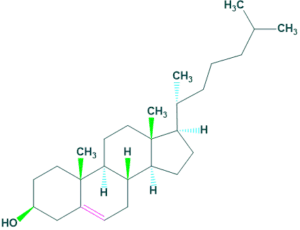
Marine sterols
- Marine sterols are natural products that are structurally and functionally similar to cholesterol.
- Most common example of marine sterol is clerosterol.
 Some other sterols are :
Some other sterols are :
Lanosterol
- It is a tetracyclic triterpenoid from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived.
- It is used in maintaining eye lens clarity.
- It functions in many biological activities such as antitumor, antiviral, antihypertensive and immunomodulatory activities.
 Lupeol
Lupeol
- It is a pentacyclic triterpenoid that is lupane in which the hydrogen at the 3-beta position is substituted by a hydroxy group.
- It is found in the skin of lupin seeds, in the latex of fig trees and of rubber plants.
- It is also occur in many edible fruits and vegetables.
 Oleanolic acid
Oleanolic acid
- It is a triterpenoid natural product occur in many plant sources such as olive oil, garlic and apple peel.
- It play role in many biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects.
 2. Sex hormones:
2. Sex hormones:
The core structure of steroids containing ketonic or hydroxyl group and mostly contain two carbon side chain.
Androgens:
It is a male sex determination steroids hormone.
For example: testosterone
 Estrogens:
Estrogens:
It is a female sex determination hormone.
For example: Estrone and Estradiol
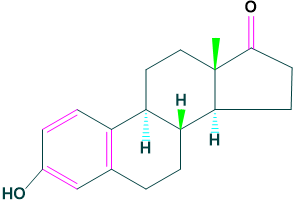
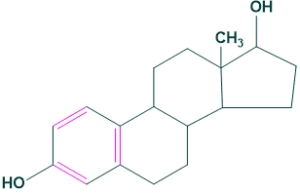
Progestogens:
These are originated from both ovaries and placenta. They maintain menstrual cycle and maintain pregnancy.
For example: Progesterone
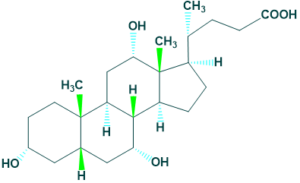
 3. Bile acids:
3. Bile acids:
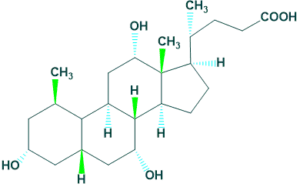
The core structure of steroid containing a five carbon side chain ending with a carboxylic acid.
For example : cholic acid and Deoxycholic acid
4. Cardiac glycoside:
In cardiac glycoside steroid R is a lactone ring.
For example: Digoxin
 5. Sapogenin:
5. Sapogenin:
In sapogenin steroid R contains an oxacylic (etheral) ring system.
For example: Digitonin
 Classification on the basis of number of carbon atoms:
Classification on the basis of number of carbon atoms:
1.Gonane:
It contains 17 carbon atoms in its structure. For example: Desogestrel
 2.Estrane:
2.Estrane:
It contains 18 carbon atoms in its structure. For example: Estradiol
 3.Andrastrane:
3.Andrastrane:
It contains 19 carbon atoms in its structure. For example: Testosterone
 4.Pregnane:
4.Pregnane:
It contains 21 carbon atoms . For example: Progesterone
 5.Cholic acid:
5.Cholic acid:
It contains 24 carbon atoms. For example: Cholic acids
 6.Cholestane:
6.Cholestane:
It contains 27 carbon atoms. For example: Cholesterol
 FAQ
FAQ
What are negative effects of steroids?
- Cause difficulty in sleeping.
- Acne on skin that results in scarring.
- It causes irritability and depression.
- When steroids are injected ,nerves are damaged.
- Cause fluid retention
What is the most important steroid in the body?
Cholesterol is the most important steroid in the body. Cholesterol is the precursor of all steroids.
What are steroids made of?
The core structure of steroid is gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is consist of 17 carbon atoms which is bonded in four fused rings, three rings are six membered cyclohexane rings and one is five membered cyclopentane ring.
What is the biological role of steroids?
Steroids maintain the structure and functions of cellular membranes and play a important role in maintaining growth and development.
 Classification of steroids:
Classification of steroids: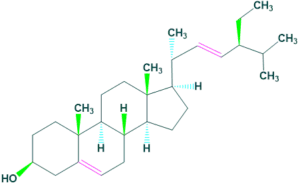 Mycosterols
Mycosterols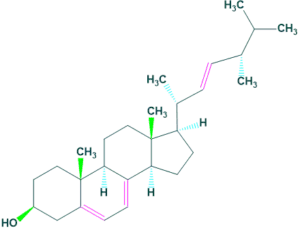 Zoosterols
Zoosterols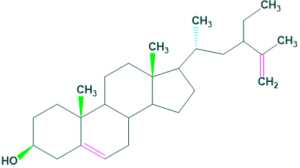 Some other sterols are :
Some other sterols are :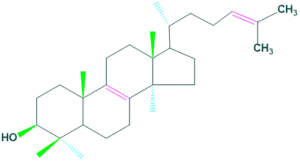 Lupeol
Lupeol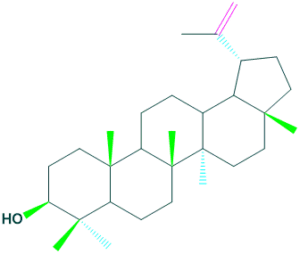 Oleanolic acid
Oleanolic acid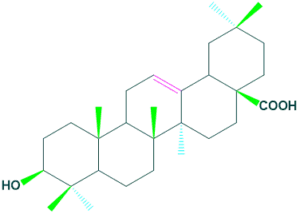 2. Sex hormones:
2. Sex hormones: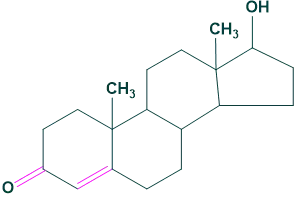 Estrogens:
Estrogens: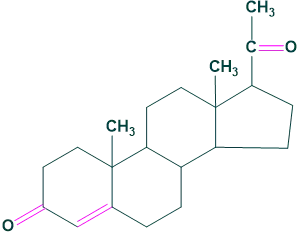 3. Bile acids:
3. Bile acids: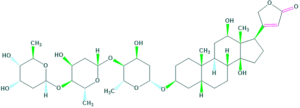 5. Sapogenin:
5. Sapogenin: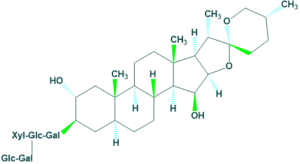 Classification on the basis of number of carbon atoms:
Classification on the basis of number of carbon atoms: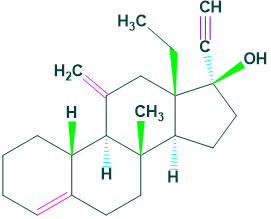 2.Estrane:
2.Estrane: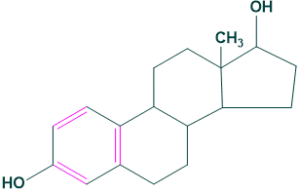 3.Andrastrane:
3.Andrastrane: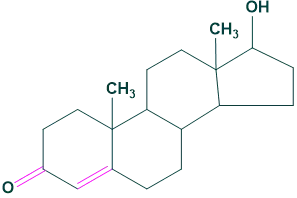 4.Pregnane:
4.Pregnane: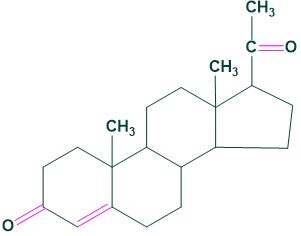 5.Cholic acid:
5.Cholic acid: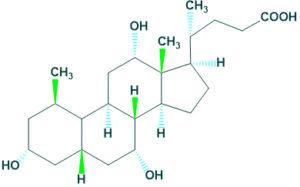 6.Cholestane:
6.Cholestane: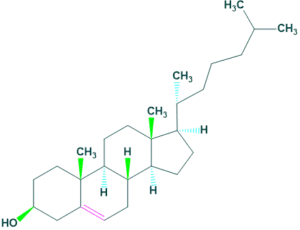 FAQ
FAQ