Polysaccharides:
Carbohydrates composed of ten or more monosaccharide units held together by glycosidic bonds are called polysaccharides. These are colloidal in size. It is known as “glycans.” These are classified in two groups
- Homo Polysaccharides.
- Hetero Polysaccharides.
Homo Polysaccharides:
These polysaccharides is made up of several units of the same type of monosaccharides unit only
OR
Homopolysaccharides on hydrolysis give only the same type of monosaccharides. e.g., glucans are polymers of glucose, and fructosans are polymers of fructose. It is known as homoglycans. Starch, dextrin, glycogen, cellulose, and inulin are the types of homo polysaccharides.
Starch :
It is the storage form of glucose in plants. It is a homo polymer composed of D-glucose units held by an α glycosidic bond known as glycosan or glycan. It consists of two components: amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose:
Amylose is a linear polymer of D-glucose units joined by α (1→4) glycosidic linkages.
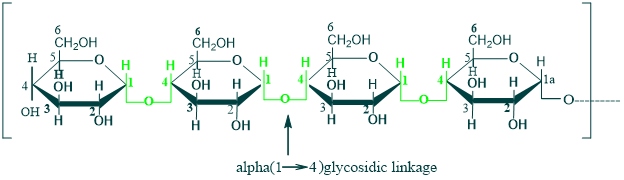
Amylopectin:
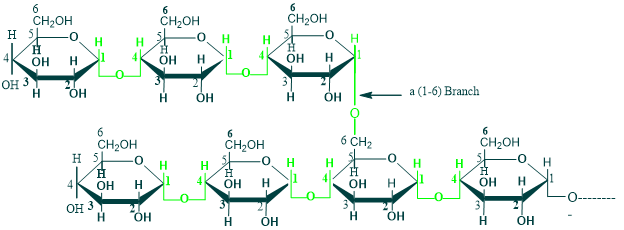
Amylopectin is a linear and branched polymer of D-glucose held by α (1→4) and α (1→6) glycosidic linkages.
Dextrin:
Partial hydrolysis of starch by acids or α-amylase(enzyme)produces substances known as dextrins. these are all occur in honey. All dextrins have a few free aldehyde groups and can show mild reducing property. They are not fermented by yeast, e.g. erythrodextrin and amylodextrin.
Glycogen:
It is the storage form of glucose in animals, found mostly in liver and muscle. The structure of glycogen is similar to that of amylopectin ,except it is more highly branched.
Function of glycogen:
- Glycogen is the source of energy for muscle.
- liver glycogen is concerned with storage and maintenance of blood glucose.
Cellulose:
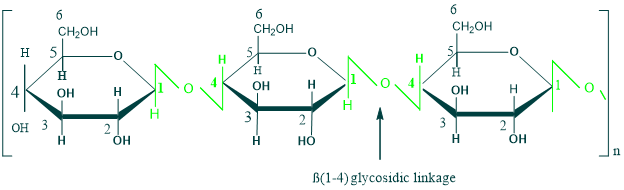
The main component of plant cell wall is cellulose. It is an unbranched polymer of β-D glucose and consist of long chains which are linked by β(1→4) glycosidic linkage. Humans lack an enzyme cellulase that can hydrolyze the β(1→4) glycosidic linkage, so cellulose is not digestable by humans.
Inulin:
Inulin is a polymer of D-fructose linked together by β(1→2) glycosidic linkage. inulin is not hydrolyzed by
α-amylase but it is hydrolyzed by inulinase, which is not present in human and so it is not utilized as food. It occurs in the some tubers of some plants , e.g. chicory, bulb of onions and garlic.
Hetero polysaccharides:
When polysaccharides are composed of different types of monosaccharides are called hetero polysaccharides.
It is also known as heteroglycans, glycosaminoglycans (GAG), or mucosa polysaccharides.
Structure of GAG:
A GAG is an unbranched heteropolysaccharide made up of repeating disaccharides.
- One component will always be amino sugar (glycosaminoglycans), D-glucosamine, or D-galactosamine.
- and other component of the repeating disaccharides is uronic acid, L-glucuronic acid or its epimer L-iduronic acid
- GAG is a polymer of [uronic acid-amino sugar]n. This polymer is attached covalently to extracellular proteins called core proteins to form proteoglycans.
- The proteoglycan monomer associates with a molecule of hyaluronic acid to form proteoglycan aggregates; the resulting structure looks like a “bottle brush.”
Occurrence of GAGs:
Heteropolysaccharides are found in the
- Synovial fluid joints
- Vitreous humor of the eye
- Artery Walls
- Bones
- Cartilage
Functions of GAGs:
- GAGs are the main component of the extracellular matrix
- GAGs have carboxyl and sulfate groups attached to them, giving them a negative charge, and possess a unique capacity to bind big quantities of water, creating a matrix that resembles gel. It acts as a shock absorber for mechanical shocks.
- They serve as “molecular sieves,” sorting and separating.
- They also give elasticity to cartilage, permitting compression and re-expansion.
- They lubricate joints both at the surface of cartilage and in synovial fluid.
Types of GAGs or Heteropolysaccharides:
- Hyaluronic acid
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Keratin sulfate
- Dermatan sulfate
- Heparin
- Heparin sulfate
Polysaccharide foods:
- Starch: Starch is a polysaccharide composed of glucose units linked together. It is a common carbohydrate found in many plant-based foods, such as:
- Potatoes
- Rice
- Wheat
- Corn
- Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
- Glycogen: Although not a direct dietary source, glycogen is a polysaccharide stored in the muscles and liver of animals, including humans. When you consume animal products like meat, you indirectly get small amounts of glycogen.
- Fiber: Dietary fiber consists of various polysaccharides that the human digestive system cannot break down. It’s found in plant-based foods, such as:
- Fruits (especially apples, pears, berries)
- Vegetables (broccoli, carrots, spinach)
- Whole grains (oats, barley, quinoa)
- Legumes (chickpeas, lentils, black beans)
- Cellulose: Cellulose is a type of fiber found in the cell walls of plants. It provides structural support to plants and is present in foods like:
- Celery
- Cabbage
- Broccoli
- Whole grains
- Hemicellulose: Another type of plant cell wall polysaccharide, hemicellulose, is found in various plant foods, including:
- Bran (outer layer of grains)
- Whole grains
- Nuts and seeds