Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides examples are trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses and heptoses, octose and nonose. It contains an aldehyde functional group called aldoses sugar and it contains a ketone functional group in its structure that is called ketoses sugar. These are the carbohydrates and they have a general formula (CnH2O)n and cannot be further hydrolyzed.
- They are the simplest form of sugar.
- They consist of a single polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones (single unit)
- They are soluble in water
- They are sweet
- They cannot be hydrolyzed into further simplest sugars.
Types of Monosaccharides:
These are two types based on functional groups.
- Aldose Sugar
- Ketose Sugar
Aldose Sugar
When the functional group is aldehyde it is called aldose sugar
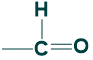
Glyceraldehyde
Glyceraldehyde is a triose (3C) monosaccharides that contain aldehyde functional groups in their structure. Glyceraldehyde
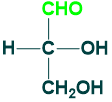
Erythrose
Erythrose is a tetrose ( 4C )sugar that contains aldehyde functional groups in its structure. Its 4-phosphate is an intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism.
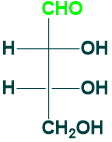
Ribose:
Ribose is (5C) aldose sugar also known as pentose sugar.
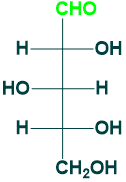
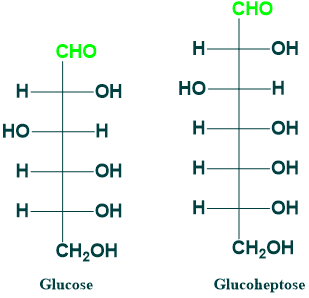
Glucose and Glucoheptose:
Glucose is (6C) aldose sugar While glucoheptose is a (7C) aldose sugar.
Ketoses Sugar:
When a functional group is ketone is called ketoses sugar.
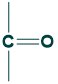
Examples of Ketoses sugars.
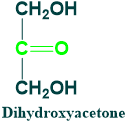
Dihydroxyacetone:
- It is found in cells as a phosphate
- Its 1-phosphate is an intermediate in glycolysis
- It is 3C ketose sugar
- It is also known as triulose.
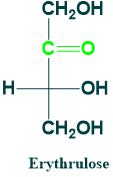
Erythrulose:
It is 4C ketose sugar. It is also known as cellulose.
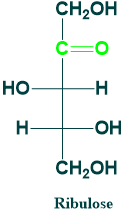
Ribulose:
- It is 5C ketose sugar.
- It is produced during metabolism
- It is an important metabolite in hexose monophosphate shunt
- It is also known as pendulous.
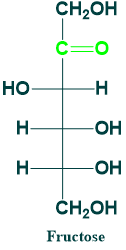
Fructose:
- It is 6C ketose sugar
- It is present in honey and fruits in the form of sucrose and inulin
- Its phosphates are intermediates of glycolysis
- It is also known as hexulose.
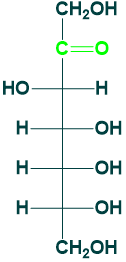
Sedoheptulose:
- It is (7C) ketose sugar
- It is found in plants
- Its 7-phosphate is an intermediate in hexose monophosphate shunt and photosynthesis.
- It is also known as cellulose.
Types of Monosaccharides Based on Number of Carbon Atoms:
Based on the number of the carbon atom, if an aldehyde group is present then these are regarded as trioses(3C), tetroses(4C), pentoses,(5C) hexoses,(6C), heptoses (7C), octoses(8C), nonoses(9C).
If Ketone group present then these are triulose(3C), tetrulose(4C), pentulose(5C), hexulose(6C), heptulose(7C) ,heptulose(8C), nonulose(9C).
Structure of Glucose and Fructose:
Glucose and fructose are the monosaccharides sugar and they are most important as a physiologically and medically. The structure of glucose and fructose can be represented in the following ways.
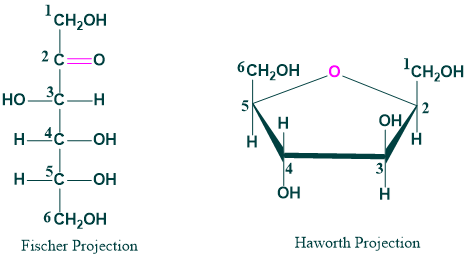
- The straight chain structural formula (Fisher Projection)
- Cyclic formula (Ring Structure or Haworth Projection)
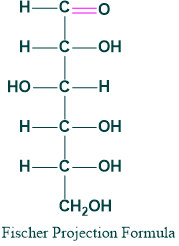
Fischer Projection of Glucose:
A 2D representation of the molecule is called fisher projection. The representation of glucose is the following
Ring Structure or Haworth Projection:
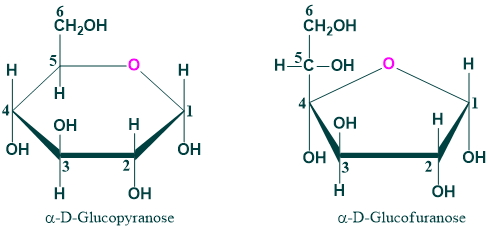
- Monosaccharide in solution is mainly present in ring form. In solution, a monosaccharide’s aldehyde (CHO) or ketone (C=O) group combines with its hydroxy (OH) group to generate hemiacetal or hemiketal respectively
- The alcohol (OH) group of C-5 and the aldehyde group of glucose at C-1 combine to produce the six-membered ring structure known as glucopyranose. Similarly, if the alcohol (OH) group at C-4 and the aldehyde group of glucose at C-1 react to create glucofuranose.
- However in case of glucose , six membered glucopyranose is much more stable than furanose ring. In case of fructose the more stable form is fructofuranose.
Fischer and Haworth Projection of Fructose:
There is 2D representation of fructose structure or Fischer Projection and Haworth Projection:
Identification Test Of Monosaccharides:
A chemical test known as the Barfoed’s test is used to identify the presence of monosaccharides and can identify reducing monosaccharides when disaccharides are present


Informative websites