Order of Inductive Effect
The order of inductive effect depends upon the electron density, withdrawal, or donation ability from a molecule. The groups which have high electronegativity can withdraw electrons, so they have a strong inductive effect. However, those groups that have lower electronegativity can donate electrons, so they have a weak inductive effect.
The following groups are showing the order of inductive effect:
Acidic and basic nature due to inductive effect
- The acidic and basic nature of various compounds can be determined by the inductive effect.
- Electron-withdrawing groups have a more acidic nature and less basic nature due to the decrease in electron density.

- While electron-donating groups have a more basic nature but a less acidic nature because of the increase in electron density.
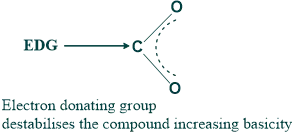
2. The acidity and basicity of a compound can also be determined based on the type of inductive effect.
- The acidity of a compound is decreased by the +I effect of the group. While the acidity of a compound is increased by the -I effect of the group.
- The basicity of a compound is increased by the +I effect of the group. While the basicity of a compound is decreased by the -I effect of the group.
Inductive Influence on Stability of Molecules
According to the inductive effect, the stability of the resulting molecule is greatly influenced by both the charge on a specific atom and the charge on a group linked to the atom.
A group with the -I effect can be attached to a positively charged atom, reducing the stability of the resulting molecule by amplifying its positive charge. However, when an atom with a negative charge is introduced to a group that exhibits the -I effect, the charge difference is much reduced, and the resulting molecule is stable due to the inductive effect.
Difference between Inductive Effect and Resonance Effect
The main difference between the Inductive and resonance effects is given below:
Inductive Effect | Resonance Effect |
|---|---|
.The Inductive Effect is created by the passage of electric charges between atoms in a molecule. | The resonance effect is created by the transfer of electron pairs between atoms in a molecule. |
It happens when bonds polarize. | It happens due to the existence of both single and double bonds. |
It is influenced by the electronegativity of atoms. | It is affected by the configuration of double bonds. |