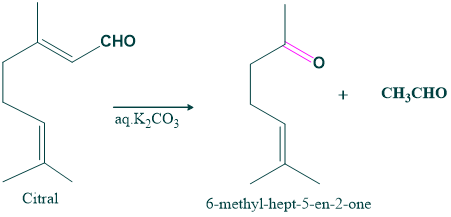What is citral?
- Citral is an acyclic monoterpene compound.
- It is made of two isoprene units.
- It is a colourless liquid.
- It is one of the major constituents of lemongrass oil.
- It exhibits geometrical isomerism about the double-bond carbons carrying methyl and aldehydic groups.
- Citral refers to two geometric isomers with names such as Geranial ( trans-citral) and Neral (cis-citral).
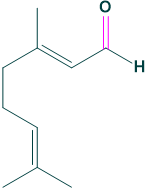
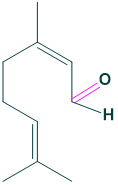

Chemical formula:
the chemical formula of citral is C10H16O
Boiling point :
Its boiling point is 77
Medicinal properties:
Citral has the properties of
- Antimicrobial
- Antioxidant
- Anticancer
- Antidiabetic
- Anti-inflammatory
Uses:
It is used extensively in the perfume and flavour industry to stimulate lemon-like odour. It is for the formation of vitamin A. Recently, it has become important as a drug for reducing blood pressure
.
Structure elucidation of citral:
- Chemical formula: C10H16O
- DBE:
The double bond equivalent of citral is 3, which indicates the presence of three double bonds in the structure of citral.
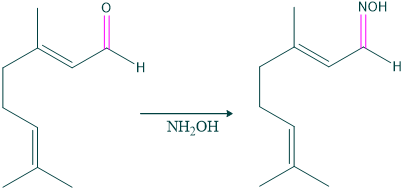
- Formation of an oxime of citral indicates the presence of an oxo group in citral.

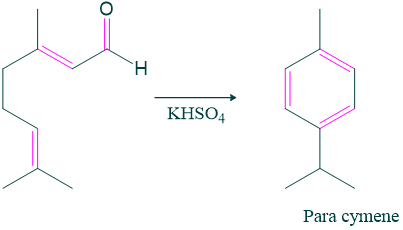
- Citral when heated with potassium hydrogen sulphate, para cymene is formed which indicates the position of methyl and isopropyl groups in citral.

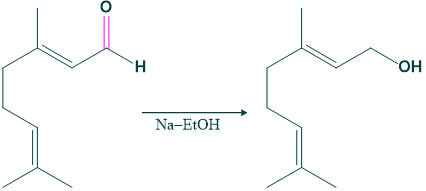
- Citral on reduction with sodium ethanol gives alcohol, which indicates the carbonyl group in citral.

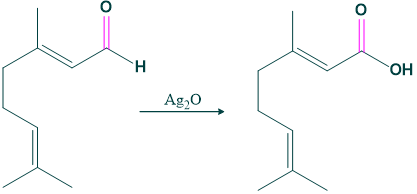
- Citral on oxidation with silver oxide gives carboxylic acid, which indicates the presence of aldehydic group in citral.

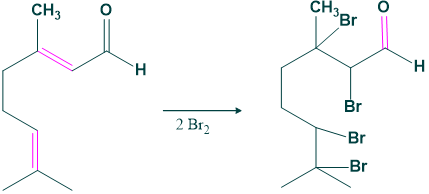
- Bromination of citral gives a brominated product which indicates the un-saturation in citral.

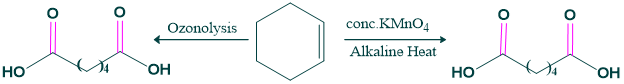
- Ozonolysis:

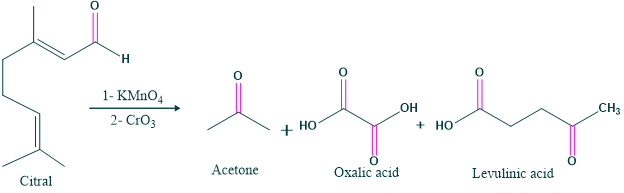
- Degradation of citral:
- Oxidation of citral in the presence of alkaline potassium permanganate and chromic acid gives acetone, oxalic acid and levulinic acid.

- Degradation of citral in the presence of aqueous potassium carbonate gives 6-methyl-hept-5-en-2-one and acetaldehyde. The synthesis of this compound confirms the structure of citral.

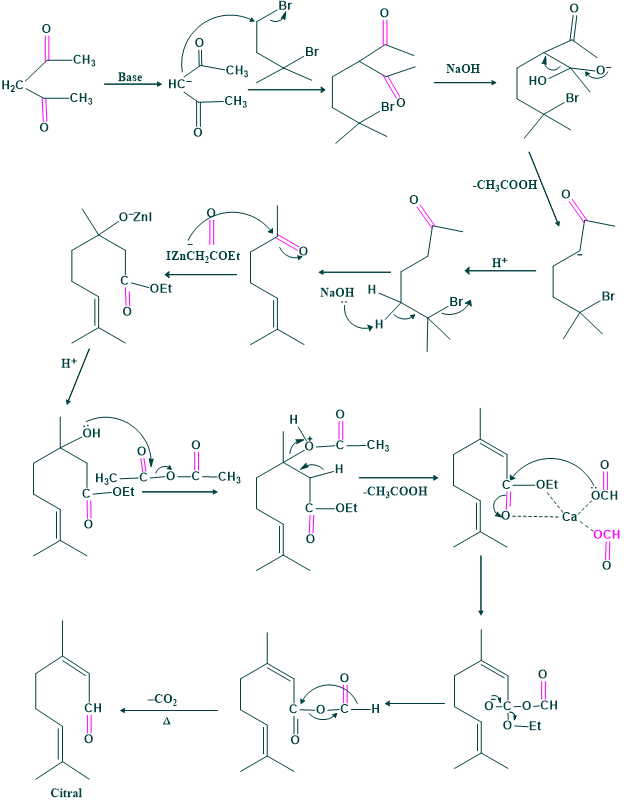
Synthesis of Citral:
Synthesis of citral was carried out by Arens et al in 1948.
The first method of synthesis:
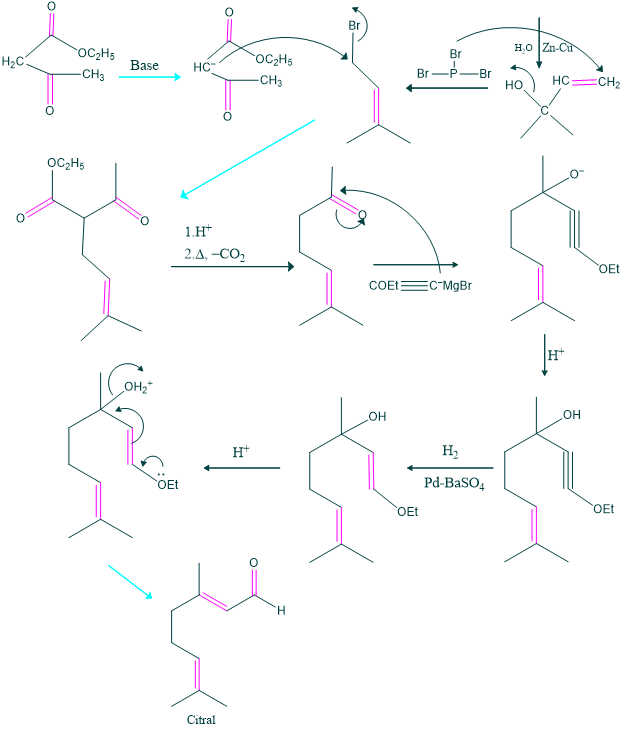
The second method of synthesis:
Frequently Asked Question
What is the purpose of citral?
It is used in the production of perfumes and other odorous substances. It is a combination or mixture of two distinct aldehydes. It is noted for its agreeable, distinct, and lemon-like pleasant odor.
Is citral temperature sensitive?
The degradation of citral is increased by high temperature, light and oxygen.
What is an example of a citral?
3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienal is the monoterpene citral which is abundantly present in the spectrum of plants and citrus fruits.

Can citral dissolve in water?
It is insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol , diethyl ether, and mineral oil.