Tautomerism
What is tautomerism? Examples of Tautomerism: Keto-Enol Form: Lactam-Lactim form: Amide-imidic acid form: Amine-Imine form: Conditions for tautomerism: Structural requirement…
Study of covalent compounds of carbon and hydrogen
(C-H) and their derivatives
What is tautomerism? Examples of Tautomerism: Keto-Enol Form: Lactam-Lactim form: Amide-imidic acid form: Amine-Imine form: Conditions for tautomerism: Structural requirement…
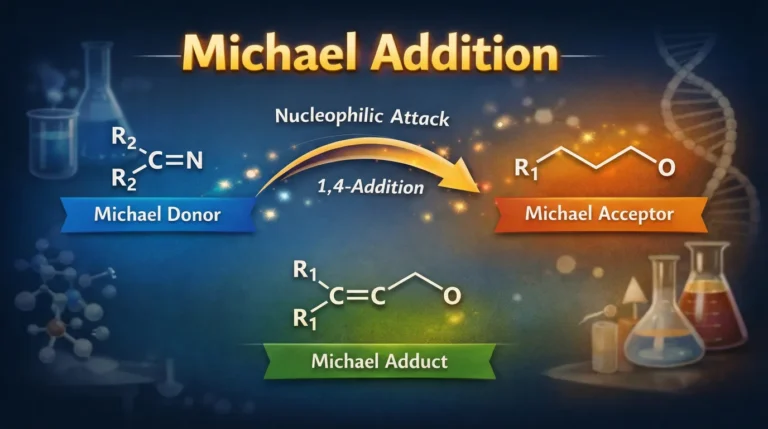
What is Michael’s Addition? The Michael addition reaction is also called the 1,4 addition reaction or conjugated addition. When a…
Cannizzaro Reaction Those carbonyl compound which donot contain α-H react in the presence of conc. base gives alcohol ( reduced…
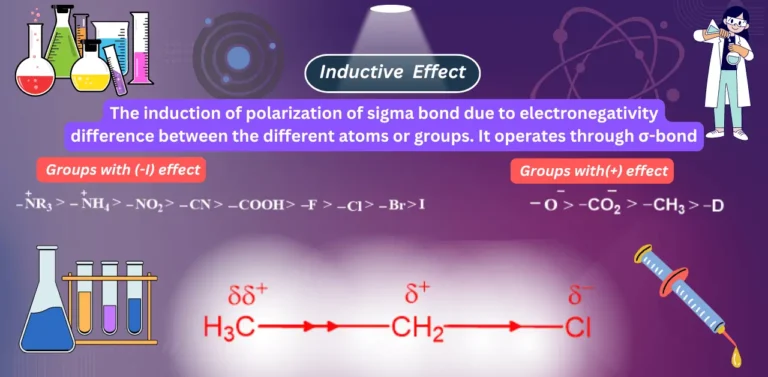
What is the inductive effect? Types of inductive groups: Groups with (-I) effect: Groups with (+I) effect: Order of Inductive…
Aldol Condensation Reaction Carbonyl compounds having α-H atom undergo a self-condensation reaction on warming with dilute acid or dilute base…
What is the resonance effect? Thus, it can be said that the -NH2 group in aniline gives electrons to the…
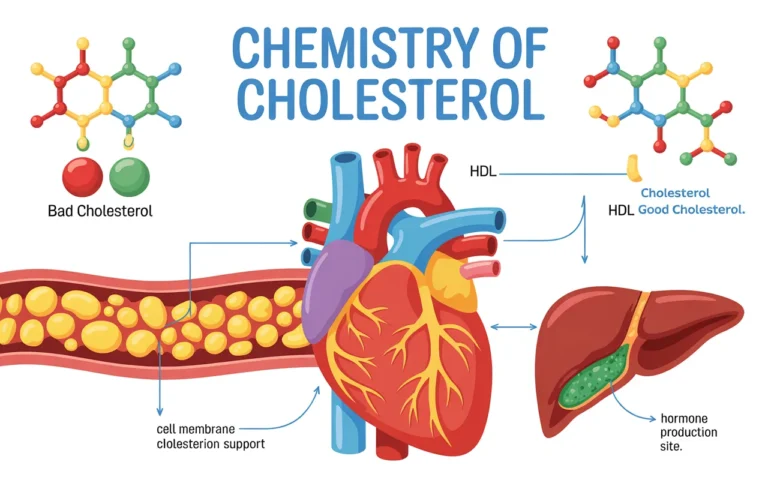
What is cholesterol? Structure of cholesterol: Sources of cholesterol: The main sources of cholesterol are the fish -liver oils, and…
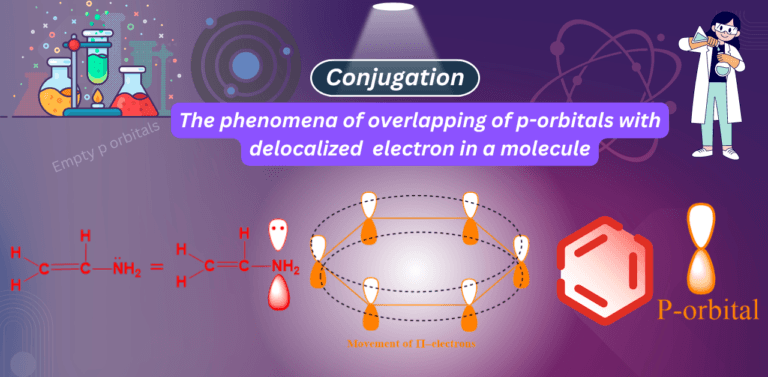
What is conjugation in chemistry? Examples of conjugation: Four examples of conjugation are given below: 1. Conjugation with empty p-orbital…
Benzil-Benzilic Acid Rearrangement Base-catalyzed reaction in which 1,2-diketone reacts with a hydroxyl ion to give a hydroxyl carboxylate ion, which…
What are steroids? Classification of steroids: 1. Sterol: These core structure of steroid ( C-17) with the aliphatic side chain…