What are proteins?
What are proteins? Proteins consist of linear sequences of amino acids that are connected by peptide bonds. The arrangement of…
Biochemistry is the branch of chemistry with the study of all chemical reactions that occur in living organism
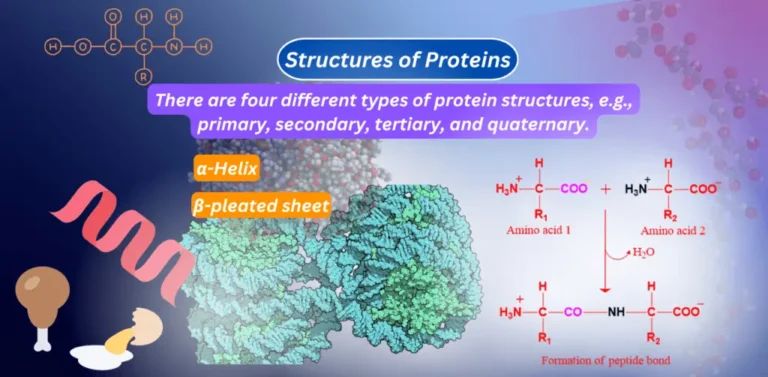
What are proteins? Proteins consist of linear sequences of amino acids that are connected by peptide bonds. The arrangement of…
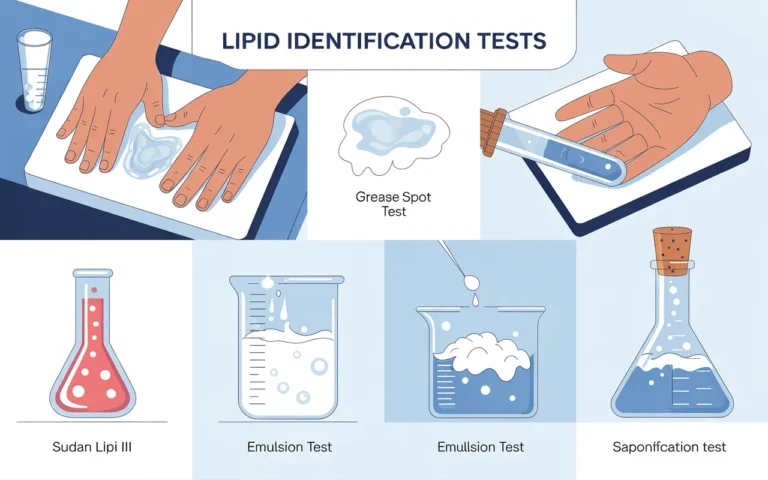
What is lipids Lipids are a diverse group of water-insoluble organic molecules, including fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and fat-soluble vitamins, crucial…
Sample collection The process of acquiring tissues, fluids, or any other sample or material for laboratory analysis is called the…

Sugar Industry The sugar industry produces one to two products and a number of byproducts, as its main function is…
ABO Blood group ABO blood group system is primarily a blood type classification system. ABO blood group test is a…
Centrifugation “Centrifugation is a technique to separate particles and components (biomolecules) suspended in a liquid medium”. How does centrifugation work…

Size Exclusion Chromatography In size exclusion chromatography ( molecular or gel filtration or gel permeation chromatography), molecules, and particles are…
SCOPE OF CHEMISTRY Everything around us deals with chemistry. When we say a thing like a scope, we come to know…
Lipids Definition Lipids are the organic compounds that can be obtained from cells and tissues by non-polar organic solvents. Lipids…

Polysaccharides: Carbohydrates composed of ten or more monosaccharide units held together by glycosidic bonds are called polysaccharides. These are colloidal…