Chromatography
What is chromatography “Chromatography” is a Greek word that means “separation of pigments, the colored substances.” This word was first…
The branch of science which deals with the composition ,structure, properties and reactions of matter. There are different branches of chemistry like organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry biochemistry, physical chemistry, industrial chemistry, nuclear chemistry
What is chromatography “Chromatography” is a Greek word that means “separation of pigments, the colored substances.” This word was first…
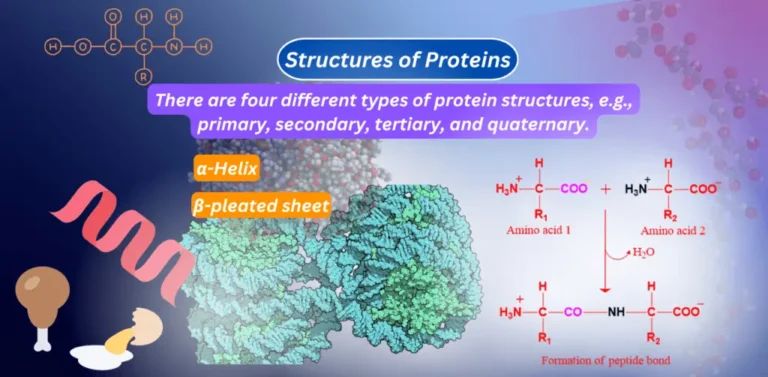
What are proteins? Proteins consist of linear sequences of amino acids that are connected by peptide bonds. The arrangement of…
What is tautomerism? Examples of Tautomerism: Keto-Enol Form: Lactam-Lactim form: Amide-imidic acid form: Amine-Imine form: Conditions for tautomerism: Structural requirement…
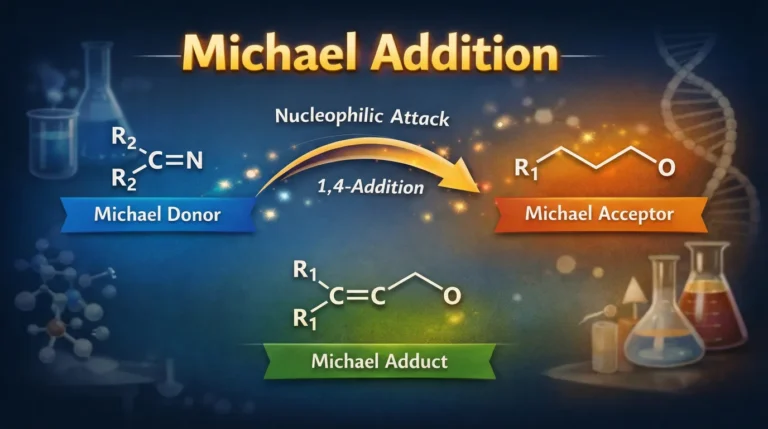
What is Michael’s Addition? The Michael addition reaction is also called the 1,4 addition reaction or conjugated addition. When a…
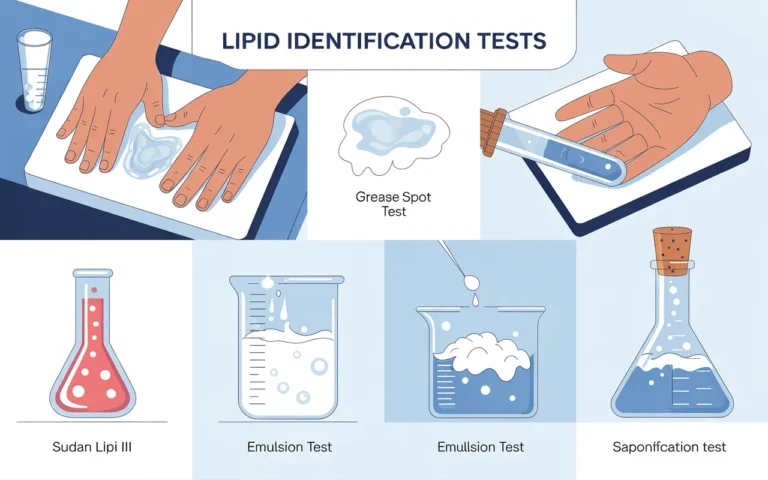
What is lipids Lipids are a diverse group of water-insoluble organic molecules, including fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and fat-soluble vitamins, crucial…
Sample collection The process of acquiring tissues, fluids, or any other sample or material for laboratory analysis is called the…
Cannizzaro Reaction Those carbonyl compound which donot contain α-H react in the presence of conc. base gives alcohol ( reduced…
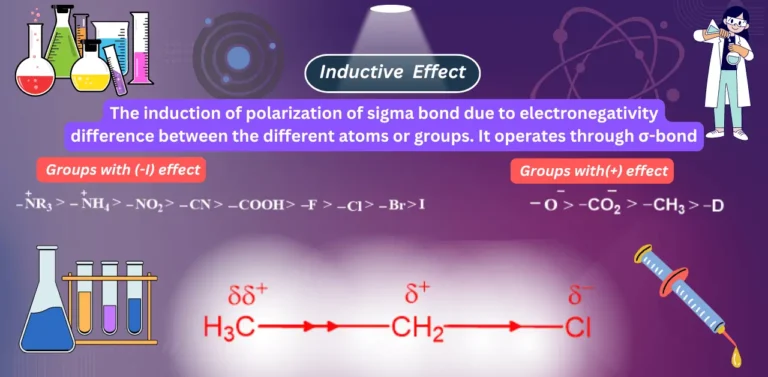
What is the inductive effect? Types of inductive groups: Groups with (-I) effect: Groups with (+I) effect: Order of Inductive…
Aldol Condensation Reaction Carbonyl compounds having α-H atom undergo a self-condensation reaction on warming with dilute acid or dilute base…
What is the resonance effect? Thus, it can be said that the -NH2 group in aniline gives electrons to the…