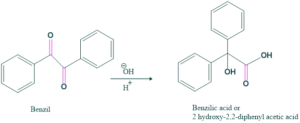
Base-catalyzed reaction in which 1,2-diketone reacts with a hydroxyl ion to give a hydroxyl carboxylate ion, which on acidification yields a hydroxycarboxylic acid. This rearrangement is called benzil-benzilic acid rearrangement. This shows intramolecular disproportionation because the carbon center is oxidized while the other is reduced.
Ketone having no adjacent enolizable proton gives this rearrangement; otherwise, aldol condensation takes place.
Reaction:
Mechanism:
This reaction occurs in four ways, as follows:
Step 1: Nucleophilic addition:
In this step, base (OH) attacks on one of the carbonyl groups of ketone and nucleophilic addition takes place as follows;
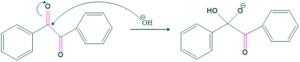
Step(2)
In this step 1,2-phenyl shift takes place.
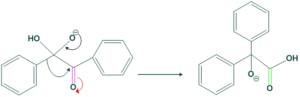
Step(3):
In this step intramolecular proton shift takes place and stable ion is obtained.
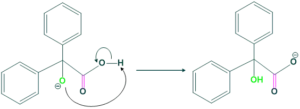
Step(4):
In this step, the carrying oxygen atom abstracts the proton to form α-hydroxyl carboxylic acid derivatives
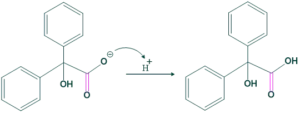
Application of benzil-benzilic acid rearrangement:
Application of benzil to benzilic acid rearrangement as follows:
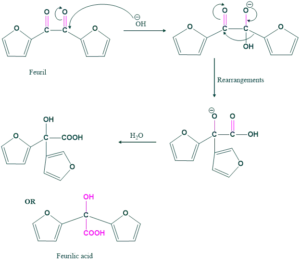
- Preparation of feurilic acid from feuril
- synthesis of α-hydroxy pentane carboxylic acid
Preparation of ferulic acid:
Ferulic acid preparation is the same as the benzilic acid preparation mechanism.
Reaction:

Mechanism:
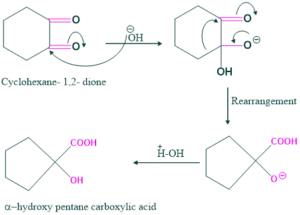
Synthesis of α-hydroxy pentane carboxylic acid:
Cyclic alkane 1,2-diketone is involved in the ring contraction, e.g. when cyclohexane 1,2-diketone is treated with base give α-hydroxy pentane carboxylic acid as follows:
Reaction:
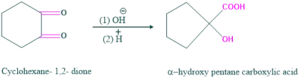
Mechanism: