Organic compounds having saturated carbon atoms are called alkanes. It contains sp3 hybridized carbons with all σ bonds and is the least reactive compound of the organic family. They are also called paraffin (waxy).
Introduction:
Alkanes are saturated organic compounds that possess carbon and hydrogen with a single covalent bond. They consist of a series called homologous series and contain the general formula CnH2n+2. Alkanes are also called paraffins; paraffins are waxy and flammable substances. Alkanes are saturated compounds and are less reactive than alkene and alkynes. Alkanes are divided into three main subdivisions: 1. Chain alkanes 2. Branched alkanes 3. Cyclic alkanes
The simplest alkane is called methane (CH₄).
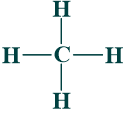
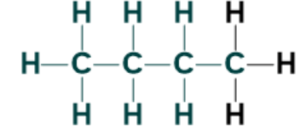
Alkanes and their molecular formulas:
| Methane | CH₄ |
| Ethane | C2H6 |
| propane | C3H8 |
| Butane | C4H10 |
| Pentane | C5H12 |
| Hexane | C6H14 |
| Heptane | C7H16 |
| Octane | C8H18 |
| Nonane | C9H20 |
| Decane | C10H22 |
Isomers of alkanes:
As we know, carbon tends to make four bonds; for example, in the methane structure, carbon forms bonds with four hydrogens. This means there is only one possible structure for a single carbon having four hydrogens. Similarly, if there are two hydrogens, then there will be two possible structures for that compound. Similar is the case if there are three carbons. Now if we talk about compounds having more than three carbons then there will be more than one possible structure for that compound. For example, C₄H₁₀ has two possible structures: butane and isobutane. Both compounds have the same chemical but different structural formulas, which is why they are called isomers.
Physical properties of alkanes:
Physical properties of organic compounds depend upon intermolecular forces for example hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, etc. These forces are found between nonpolar molecules that are closer to each other. These forces are directly proportional to the size of the molecules and are more dominant in straight-chain organic compounds than in branched chains.
Physical appearance:
The simplest alkanes are colorless gases (i.e., C1 to C4); alkanes having C5 to c 17 carbon atoms are generally colorless liquids, and higher alkanes having C18 or more than 18 carbons are colorless solids.
Melting point:
melting point of alkanes increases with increments in carbon numbers likewise boiling point which also increases as we go higher alkanes. But the point to be noted is that branched-chain alkanes have relatively higher melting points than straight-chain alkanes, the reason is that the intermolecular forces also depend on the crystal lattice fitness of the molecule other than its size. So, larger and well-packed alkanes are difficult to disturb, and more energy will be required to open or disturb that structure.
| methane | -183 |
| ethane | -172 |
| propane | -188 |
| n-butane | -138 |
| n-pentane | -130 |
| n hexane | -95 |
| n-heptane | -91 |
| n-octane | -57 |
| n nonane | -54 |
| n decane | -30 |
| n undecane | -26 |
| n dodecane | -10 |
Boiling point:
The boiling point of alkanes increases regularly with the addition of each carbon atom. As we move towards higher alkanes the difference between boiling points decreases. straight-chain alkanes have high boiling points as compared to straight-chain alkanes. Long-chain alkanes are found to be more flexible and stronger. So, it is difficult to break them as compared to branched-chain alkanes. More heat energy will be required to break straight-chain alkanes as compared to branched-chain alkanes.
| Alkanes | boiling point |
| Methane | -163 |
| Ethane | -89 |
| Propane | -42 |
| Butane | 0 |
| Pentane | 36 |
| Hexane | 69 |
| Heptane | 98 |
| Octane | 126 |
| Nonane | 151 |
| Decane | 174 |
Solubility:
The solubility of a solute in a solvent depends upon its strength of intermolecular forces with that of solvent molecules. If the intermolecular forces between solute and solvent are greater than the forces between the ions of solute and solvent themselves, then the solute is said to be soluble in solvent. As alkanes consist of entirely covalent bonds and are non-polar and the rule says that LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE, so alkanes are soluble in non-polar solvents such as carbon tetrachloride, ether, and C6H6 and are insoluble in the polar solvents.
Density:
As the molecular weight of alkanes increases the density increases. density increases with molecular weight until its value reaches 0.8. All the alkanes are much lighter than water that’s why petroleum floats on the water surface.
Alkanes nomenclature:
In the earliest days, compounds were given names based on the substance in which they were found or based on the name of the person who discovered them. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry has devised a rule for systematically naming organic compounds. The nomenclature of alkanes consists of 4 main parts, locant, prefix, parent, and suffix.