[ez-toc]
Synthesis of sugar is a very important industrial process because sugar is a sweetening agent used in daily life meals. It is chemically sucrose which is a disaccharide (a carbohydrate). Various sources can be used for the synthesis of sugar like sugarcane, date palm, root beet, maple, etc. Here we are going to discuss its formation from sugarcane.
Stepwise process of sugar synthesis from sugarcane is described below:
Step 1: Extraction of sugarcane juice
Sugarcane juice contains sucrose and water so to obtain sugar (sucrose) firstly we have to extract sugarcane juice. For this follow the following steps:
Screening of sugarcane:
If we look at the crop of sugarcane, we see that sugarcane is a long plat that is covered by leaves as:

In screening remove these leaves and soil if it is attached to sugarcane. The purpose of this step is to remove field trash, soil, and rocks.
Washing of sugarcane:
Wash sugarcane with water to remove water-soluble impurities from it. The purpose of this step is to get neat and clean sugarcane so that clean juice can be extracted from it.
Cutting the sugarcane:
Sugarcane is cut into small pieces called chips. These chips are cut with the help of knives fitted on the horizontal shaft in a machine.
Crushing the chips:
Sugarcane chips are then crushed in a milling section to extract juice from them. The milling section usually has 5 mills and each mill has three rollers fitted in a triangular shape. One roller is present above and two below giving a triangular shape to the mill. The movement of the top roller is anti-clockwise and the movement of the bottom rollers is clockwise to improve the mill’s pressing power. Pressure increases as chips move from one mill to another to increase juice extraction efficiency. Because the efficiency of the first mill is just 50%.
 The juice extracted is greenish. The dry pulpy residue left after juice extraction is called Bagasse which can be used as fuel. It is the first byproduct of sugar synthesis.
The juice extracted is greenish. The dry pulpy residue left after juice extraction is called Bagasse which can be used as fuel. It is the first byproduct of sugar synthesis.
 Imbibition:
Imbibition:
Bagasse may also contain sucrose in it. To extract this sucrose imbibition method is applied in which bagasse is dipped in water and again fed into the milling section. Water dissolves the remaining sucrose in it and that water is extracted by milling. This is done to increase juice extraction efficiency.
Step 2:Purification of juice
The juice extracted has soluble and insoluble impurities in it. Therefore, its purification is necessary.
Removal of insoluble impurities:
To remove insoluble impurities from juice, it is strained with the help of a strainer. Because insoluble impurities are usually solid materials, so can be strained or filtered. There is another method to remove them. In this method, an adsorbent like diatomaceous earth slurry is added to the juice and then it is passed through a pressure filter. The impurities form a chemical bond or physical attraction with the adsorbent and are thus strained by a pressure filter. This process is called Pressure Filtration.
Removal of soluble impurities:
Soluble impurities are usually due to colored materials present in the juice. To remove them following steps are used:
Phosphatation:
Heat the juice and then add phosphoric acid (H3PO4). The pH of this hot liquor is adjusted at 7-7.5 by adding lime (CaO) to it. These conditions help in the formation of insoluble calcium phosphate (Ca(PO4)3) which acts as an adsorbent for the colored materials in the juice which is then removed by filtration.
Sulphation:
In this process, sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) is passed through the hot juice containing lime in it. This precipitates the colored impurities present in the juice which can be filtered now.
Carbonation:
Milk of lime is added to the hot liquor and then CO2 is passed through it, here temperature is maintained at 55-60 degrees centigrade. A chemical reaction takes place and CaCO3 precipitates along with other flocculant-type precipitates are formed. All these precipitates are removed by filtration.
Now, almost all the impurities have been removed from the juice and therefore, the juice color will be improved from greenish to brownish. The filtered impurities are collected and called Filter Mud. Filter mud is the second byproduct of sugar synthesis which is used as animal feed. This is converted into compact cake by placing it under pressure for storage purposes and now it is called Filter Cake or Mud Cake.

Step 3: Concentration of juice
The purified sugarcane juice has about 15% sucrose and 85 % water in it therefore, it has to be concentrated. To concentrate it we have to evaporate water from the juice. For this purpose, a multiple-effect evaporator is used. In multiple effects, evaporator steam is used as a heat carrier. The evaporator may have a triple or quadrupole effect. Quadrupole effect evaporator has four evaporators connected in series through a heating coil called calandria. Steam is passed through calandria boiling the juice and removing the water to concentrate the juice. The concentrated juice obtained after this is called Syrup. The concentration of sucrose in syrup is about 65%.
Step 4: Crystallization of sugar
For the crystallization process, the above solution is converted into a supersaturated solution containing 84-85% sucrose content. When this supersaturated solution is cooled crystals of sugar or sucrose are formed in the solution. This solution containing sugar crystals and liquid solution is called Massecuite.
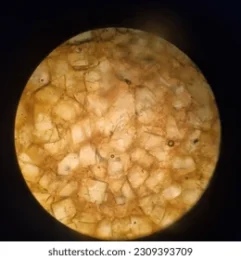
The sugar crystals from massecuite are removed by centrifugation. The mother liquor obtained after removing crystals is called Molasses. The sugar obtained has a brown color therefore called ‘Brown Sugar’ or ‘Raw Sugar’.
 Step 5: Refining of sugar
Step 5: Refining of sugar
To convert brown sugar to white sugar refining of sugar is done. For refining supersaturated solution of brown sugar is made which is called magma. Then decolorizing agents are added to magma which decolorizes it. Then solution is cooled and white colored sugar crystals are obtained after cooling. This sugar obtained is called ‘White Sugar’ or ‘Refined Sugar’.

how to crystalize sugar?
asdgfbgfdfghnhgfdefgh