What are steroid hormones?
- A steroid hormone is a steroid that functions as a hormone.
- Steroid hormones are a class of hormones derived from cholesterol that function as chemical messengers in the body.
- These are produced in the adrenal cortex, testis, ovary, and some other peripheral tissues.
- All steroid hormones originate from cholesterol but differ from each other because of the different ring structures and side chains they contain.
- Those enzymes which produce steroid hormones are present in Mitochondria and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- These are soluble in lipids but insoluble in water.
- These are permeable to cell membranes so they are not stored in cells.
- They are nonpolar so can diffuse easily through lipid membranes. Thus they leave cells instantly after synthesis.
- Steroids are derivatives of a reduced 3-ring phenanthrene molecule with a fourth “D” ring added.


[ez-toc]
Types of steroid hormones:
1. Corticosteroids:
They are made in the adrenal cortex. The binding globulin carries cortisol.
Glucocorticoid:
- These are secreted in the adrenal cortex.
- They mainly affect metabolism by
- decreasing inflammation and
- Increasing resistance to stress.
- For example
Cortisol, corticosterone, 11-dehydro corticosterone and cortisone.

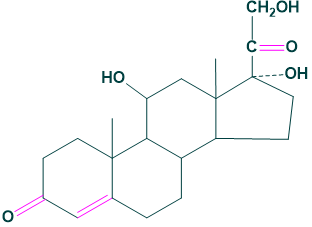
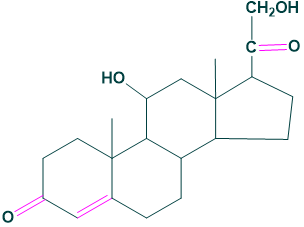
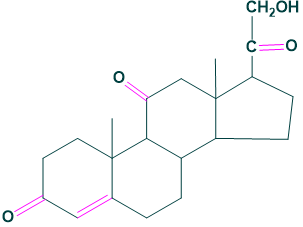
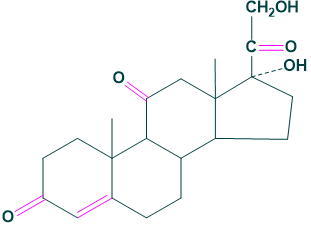
Mineralocorticoids:
- These are originated in the adrenal cortex.
- They maintain salt and water balance.
- For example
Aldosterone
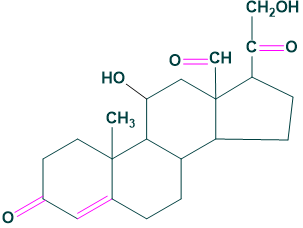
2. Sex steroids:
These are typically made in the gonads or placenta. The binding globulin carries testosterone and estradiol.
Progestogens:
- Progestogens also called progestins.
- These are originated from both ovaries and placenta.
- They mediate menstrual cycle and maintain pregnancy.
- For example
Pregnenolone and progesterone
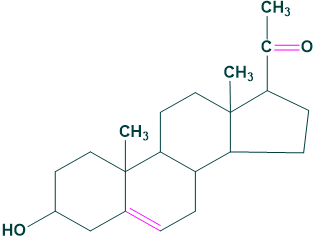
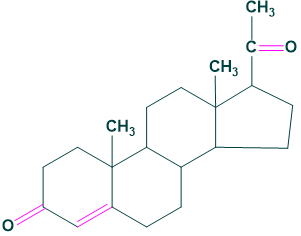
Estrogens:
- These are secreted in the adrenal cortex and gonads.
- They mainly affect maturation and functions of secondary sex organs(female sexual determination).
- For example
Estradiol and Estrone
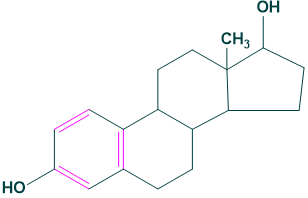
Androgens:
- These are also originate in the adrenal cortex and gonads.
- They mainly effect maturation and functions of secondary sex organs ( male sexual determination).
- For example
Testosterone
Functions of steroid hormones:
Steroid hormones play very important role in
- Carbohydrate regulation
- Mineral balance
- Reproductive functions
- Inflammatory response
- Stress response
- Bone metabolism
- Cardiovascular fitness
- Activates DNA for protein synthesis
- Immune functions
FAQ
What is the chemical structure of a steroid?
Steroids are derivatives of a reduced 3-ring phenanthrene molecule with a fourth “D” ring added. The carbons of A,B,C and D rings are conventionally numbered 1 to 17. They interact with cellular receptors.

Which food contains steroids?
- Celery
- Spinach
- Quinoa
- Eggs
- Fava Beans
- Avocados
- Extra Virgin Olive oil and coconut oil
- Foods high in vitamins C,A, and D , zinc, and magnesium.
Is cholesterol a steroid?
Cholesterol is the most common steroid in the body. It is a precursor to vitamin D and many steroid hormones such as testosterone, estrogen and cortisol.
Who is the father of steroids?
John Bosley Ziegler is the father of steroids. He was American physician who originally developed the anabolic steroid Methandrostenolone (Dianabol) which was released in the USA in 1958 by Ciba.