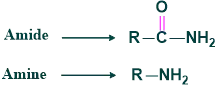
The reaction in which the conversion of amides to amine with one carbon atom less than the starting material in the presence of Br2 and KOH or alkaline Hypohalite is called Hoffmann rearrangement. This rearrangement was given by Agust Wilhem.
Reaction :

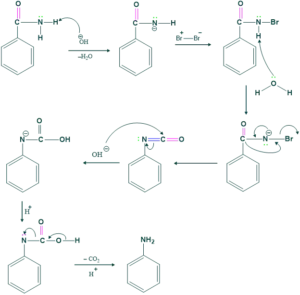
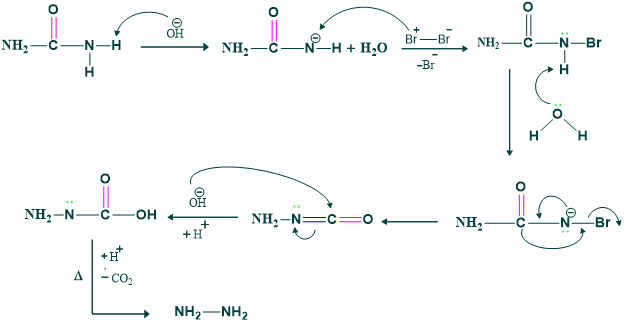
Mechanism of the Hofmann Rearrangement:
Step 1:
Deprotonation of amide by Base (OH) is done to make intermediate.

Step 2:
This intermediate reacts with Br2 to give N-bromoamide.
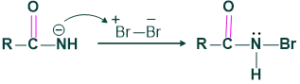
Step 3:
In this step loss of proton takes place.

Step 4:
In this step migration of R( alkyl or aryl group from adjacent carbon atom to form isocyanate.
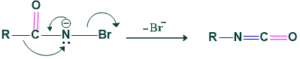
Step 5:
In this step, hydrolysis of isocyanate takes place to form carbamic acid.
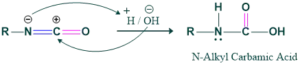
Step 6:
Here, Decarboxylation takes place to form amine.

Application of Hoffmann Rearrangment:
- Synthesis of aliphatic and aromatic amines.
- Preparation methylamine, aniline and benzylamine etc.
- Prepartion of amino acid.
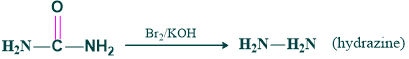
- Conversion Of urea to hydrazine.
- Synthesis of anthranilic acid.
- synthesis of 3-amino pyridine.
- synthesis of 4-amino pyridine.
Synthesis of aliphatic and aromatic amines:
We synthesis aliphatic and aromatic amines from carboxlic acid. First we convert the OH group of carboxlic acid into good leaving group and then this derivatives is converted into primary amines having carbon atom less than one starting material.
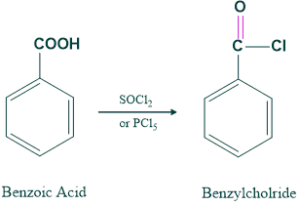
Then this benzylchloride is converted into primary amines as follows;
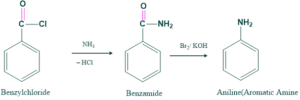
Mechanism:
Preparation of methylamine, aniline and benzylamine:
We can form methylamine , aniline and benzylamine by starting material as follos;
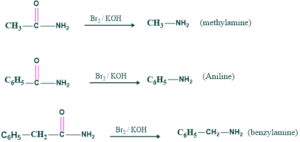
Preparation of amino acid:
β-aniline is actually an amino acid which is prepared by reacting succinamide with bromine and aqeous caustic potassium. Reaction takes place through the halo
amide of succinic acid.
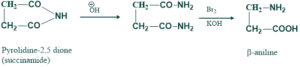
Synthesis of urea to hydrazine:
Mechanism:
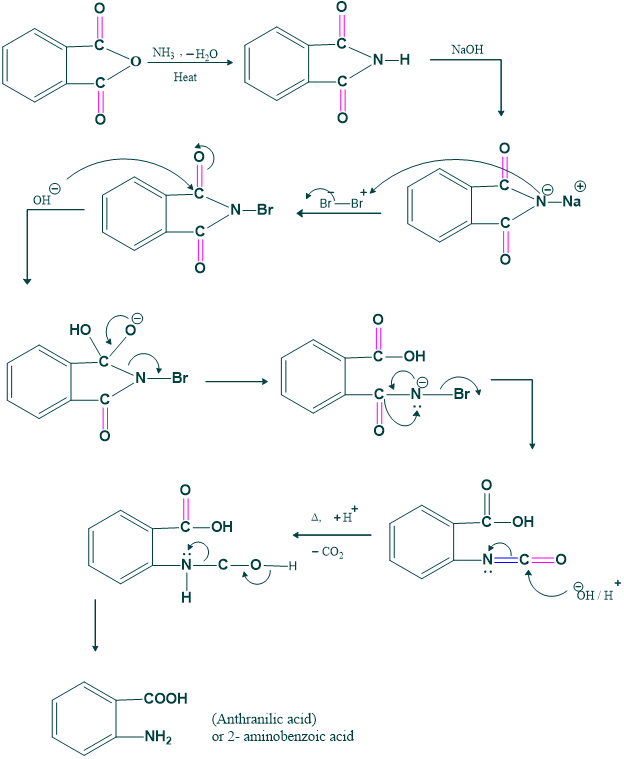
Synthesis of anthranilic acid:
We prepare anthranilic acid by this rearrangement. Anthranilic acid is basic starating material for preparation of ortho -disubstituted benzene derivative as follows;
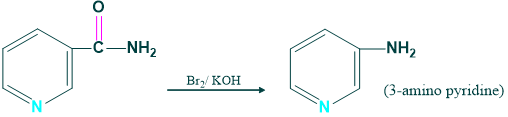
Synthesis of 3- amino acid pyridine:
We prepare 3-amino pyridine from the nicotine amide in the presence of Br2 and KOH.
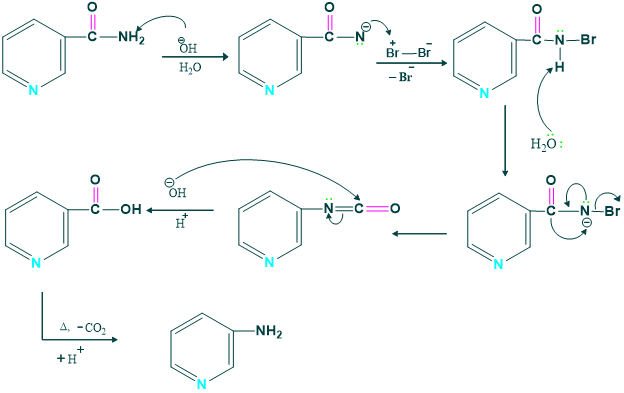
Mechanism:
3-amino pyridine is very fatal ,thus it shows
- Absorption through skin and eyes
- Destructive to mucous membrane and respiratory tract.
- On thermal decomposition it release toxic gases Due to these reason it is very fatal.
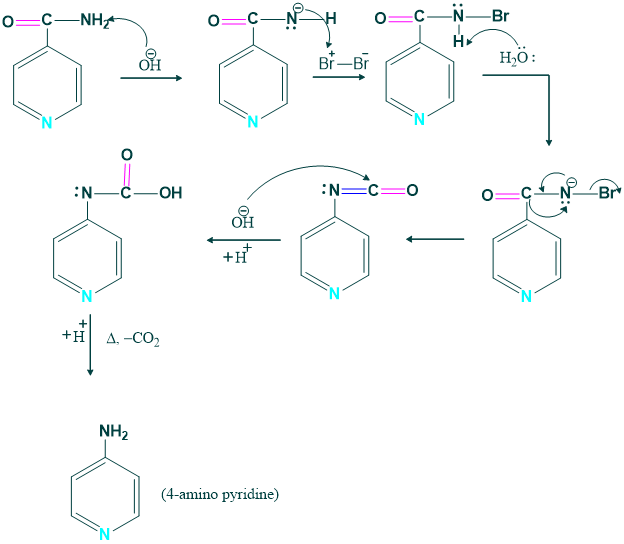
Synthesis of 4-amino pyridine:
4 amino pyridine is prepared from the pyridine carbamide.
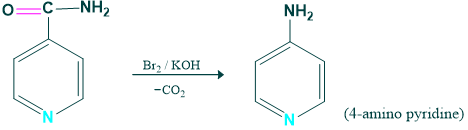
Mechanism: