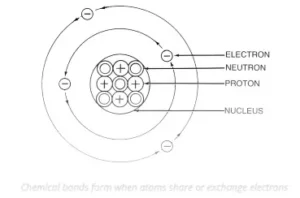
The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together and stabilises them by the overall loss of energy is known as chemical bonding.
Valence electrons play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. In the electron configuration of an atom, the outermost shell is called the valence shell, and the electrons in the valence shell (outermost shell) are known as valence electrons. Take the carbon atom for example: the electron configuration of carbon is 1s22s22p2. The outermost shell is the 2nd principal shell, so there are 4 valence electrons in carbon. Valence electrons are the electrons that are the furthest away from the nucleus, and thus they experience the least attraction from the nucleus and are the most reactive. They play the most important role in chemical bonding
Chemical bonds are forces that hold the atoms together in a molecule. They are a result of strong intramolecular interactions among the atoms of a molecule. The valence (outermost) electrons of the atoms participate in chemical bonds. When two atoms approach each other, these outer electrons start to interact. Although electrons repel each other, they are attracted to the protons within atoms. The interplay of forces results in the formation of bonds between the atoms.
Theories on Chemical Bonding:
- Lewis Theory
- Kossel’s Theory
- Fajan’s rule
- VSEPR Theory
Types of Chemical Bonding
There are four major types of chemical bonding in chemistry, which includes;
- Ionic bond
- Covalent bond
- Metallic bond
- Hydrogen bond
With the help of these bonds, the constituents like atoms and molecules can obtain a stable electronic configuration, i.e., octet configuration.
Covalent Bond:
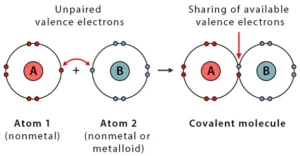
A covalent bond is the bond formed when two atoms share their electrons equally. The pair of electrons that form this bond is called a bonding pair or shared pair. Covalent bonds are known as molecular bonds. The bonding pairs ensure the stability of their outer shell by achieving 8 total electrons on this shell.
Properties of Covalent Bond:
If the normal valence of an atom is not satisfied by sharing a single electron pair between atoms, the atoms may share more than one electron pair between them. Some of the properties of covalent bonds are listed below:
- Covalent bonding does not result in the formation of new electrons. The bond only pairs them.
- They are very powerful chemical bonds that exist between atoms.
- A covalent bond normally contains an energy of about ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol).
- Covalent bonds rarely break spontaneously after it is formed.
- Covalent bonds are directional, where the atoms that are bonded showcase specific orientations relative to one another.
- Most compounds having covalent bonds exhibit relatively low melting points and boiling points.
- Compounds with covalent bonds usually have lower enthalpies of vaporisation and fusion.
- Compounds formed by covalent bonding don’t conduct electricity due to the lack of free electrons.
- Covalent compounds are not soluble in water.
How are Covalent Bonds Formed?
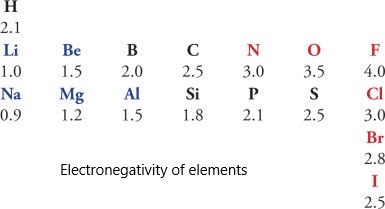
A covalent bond is formed when the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is too small (<2) for electron transfer. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms to gain more stability, obtained by sharing the outermost (valence) electrons and forming a complete electron shell.
Covalent bonds hold atoms together because the attraction between the positively charged nuclei and the negatively charged shared electrons is greater than the repulsions between the nuclei themselves. This attraction makes the molecules stable. The strength of a covalent bond is determined by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms.
Types of Covalent Bonds:
A covalent bond can be classified by the number of shared electrons, the polarity of bonds, and the coordination of the atoms.
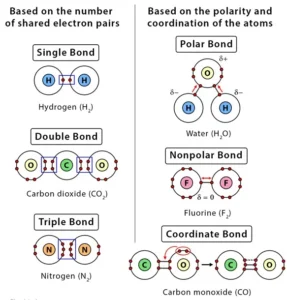
Based on the number of shared electron pairs, there are three types of covalent bonds
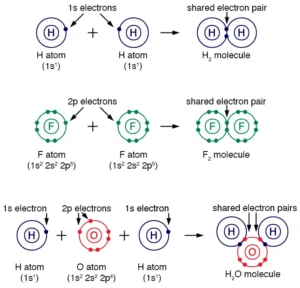
1. Single Covalent Bond:
When one pair of electrons, or two electrons, are shared between the atoms, it is known as a single covalent bond or merely a single bond.
Examples: H2, Cl2, Br2, I2, HCl, NH3, CH4, and C2H6
2. Double Covalent bond:
When two pairs of electrons, or four electrons, are shared between the atoms, it is known as a double covalent bond or double bond.
Examples: O2, CO2, SO2, and C2H4
3. Triple Covalent Bond:
When three pairs of electrons, or six electrons, are shared between the atoms, it is known as a triple covalent bond or triple bond.
Examples: N2, C2H2, and CN–
Based on the polarity of the bond and the coordination of the atoms, there can be three other types of covalent bonds:
1. Polar Covalent Bond:
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when the atoms sharing the electrons have a significant difference in their electronegativities, i.e., between 0.1 to 2. As a result, the bonded pair is attracted toward the more electronegative atom making that atom slightly negative, and the other atom becomes slightly positive.
Examples: H2O, CHCl3, CH3OH, HCl, and NH3
2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond
When the electronegativity difference between the atoms is zero, then electrons are equally shared between the atoms. In this case, the covalent bond is nonpolar.
Examples: H2, O2, N2, CO2, and CH4
Polarization of Covalent Bonds:
It is observed that in the polar bonds, the electron cloud moves closer to the higher electronegative atom. This causes a permanent dipole between the bonds. Such covalent bonds are said to be polarized. Here the higher electronegative atom will have a negative charge while the other one will be positively charged.
3. Coordinate Covalent Bond or Dative Covalent Bond
In this type of covalent bond, the shared pair of electrons comes from one of the atoms. This kind of bond is typically observed in the bonding of metal ions to ligands.
Examples: BF3.NH3, Al2Cl6, HNO3, CO, H3O+, and NH4+
The presence of a bond between two elements can be determined by calculating the electronegative value between two atoms.
| Bond Type | Electronegativity Value |
| Polar Covalent Bond | 0.5 to 1.9 |
| Non-polar Covalent Bond | 0 to 0.4 |
| Ionic Bond | 2.4 to 4.0 |
Examples of Covalent Bonds:
Here are some examples of covalent compounds [1-9]:
1. Hydrogen (H2)
Hydrogen (H) is the simplest of all elements. It has only one electron and requires another electron to achieve the electronic configuration of its nearest inert gas helium. So, two hydrogen atoms will bond together in a single bond to form a hydrogen molecule.
2. Oxygen (O2)
The valency of oxygen (O) is two, which means that it requires two electrons to complete its outermost (valence) shell. Therefore, two oxygen atoms will combine and share their two valence electrons, resulting in a double bond.
2. Nitrogen (N2)
Nitrogen (N) has five valence electrons, so it needs three more valence electrons to complete its octet. Two nitrogen atoms will combine. Each will share three electrons to form three covalent bonds, i.e., a triple bond, resulting in a nitrogen molecule.
3. Water (H2O)
A water molecule consists of two hydrogen (H) and one oxygen (O) atom. Oxygen has a valency of two, and hydrogen has only one electron in its orbital. So, each hydrogen atom will share its electron and covalently bond with the oxygen. As a result, there will be two single bonds.
4. Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide has two oxygen (O) atoms that are bonded to a single carbon (C) atom. The valency of carbon is four, and that of oxygen is two. So, each oxygen forms a double bond by sharing two of its valence electrons with the carbon. Hence, each C=O bond is a double bond.
5. Methane (CH4)
Methane is made up of one carbon (C) and four hydrogen (H) atoms. The valency of carbon is four, and that of hydrogen is one. So, each hydrogen will share its only electron and form a single covalent bond with the carbon. There will be a total of four covalent bonds in methane, all of which are single bonds.
6. Ammonia (NH3)
Nitrogen (N) has five electrons in its outer orbital and requires three more to complete its valence shell. Hydrogen (H) will share its lone electron with nitrogen, and three hydrogen atoms are required to complete nitrogen’s outermost shell. This sharing of electrons results in three single covalent bonds.
7. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
The carbon monoxide molecule is represented by three covalent bonds between the carbon (C) and oxygen (O) atoms. Carbon has a valency of four and will require four electrons to complete its outermost shell. Oxygen has a valency of two and requires two electrons to complete its outermost shell. Therefore, a regular double bond will form between the two atoms. Carbon is left with a deficit of two electrons, which will come from oxygen as it already has lone pairs. As a result, the third covalent bond will be a coordinate covalent bond.
Pure Covalent Bonds:
By definition, a pure covalent bond is one that exists between two atoms with the same electronegativities. Thus, a pure covalent bond does not display any ionic character. Diatomic elements are perfect examples of pure covalent bonds because both atoms evenly share the electrons.
Examples: H2, O2, and N2
Ionic Bond:
The electrostatic force of attraction which holds the two oppositely charged ions together is called the ionic bond.
A chemical bonding is formed between two atoms by the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to the other as a result of which the atoms attain their nearest inert gas configuration
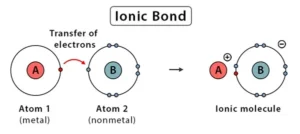
There are primarily three ways in which two atoms combine to lose energy and to become stable. One of the ways is by donating or accepting electrons to complete their octet configuration. The bond formed by this kind of combination is known as an ionic bond or electrovalent bond. This kind of bond is formed when one atom gains electrons while the other atom loses electrons from its outermost level or orbit.
Electrovalent Bond:
Electrovalent bonds are produced when electrons are transferred from atoms of one element to atoms of another element, producing positive and negative ions. The bond which is formed by the transfer of electrons between the atoms is called electrovalent bond or ionic bond. Electrovalent bonds are only formed between metals and non-metals. Electrovalent bonds are not formed between two non-metals.
In simple words electrovalent bond involves the transference of a certain number of electrons to another dissimilar atom which has a tendency to gain electrons so that both acquire stable inert gas configurations. The electrostatic attraction always tends to decrease the potential energy. Hence, the potential energy of the system is much less than it was before the formation of an ionic bond.
Electronegativity and Ionic Bonding:
- An Ionic bond is the bond formed by the complete transfer of valence electron to attain stability.
- This type of bonding leads to the formation of two oppositely charged ions – positive ions known as cations and negative ions known as anions.
- The presence of two oppositely charged ions results in a strong attractive force between them. This force is an ionic or electrovalent bond.
- Ionic bonds form between atoms with large differences in electronegativity, whereas covalent bonds formed between atoms with smaller differences in electronegativity.
- The compound formed by the electrostatic attraction of positive and negative ions is called an ionic compound.
Ionic Bond Properties:
Due to the presence of a strong force of attraction between cations and anions in ionic bonded molecules, the following properties are observed:
- The ionic bonds are the strongest of all the bonds.
- The ionic bond has charge separation, and so they are the most reactive of all the bonds in the proper medium.
- The ionic bonded molecules have high melting and boiling point.
- The ionic bonded molecules in their aqueous solutions or in the molten state are good conductors of electricity. This is due to the presence of ions which acts as charge carriers.
Examples of Ionic Bonds:
The following table shows the elements and the ions formed by them when they lose or gain e‑.
| Element | Electronic config. | Reaction | Formed ion |
| Na(11) | 2,8,1 | Na → Na+ + e– ………………….. Reaction 1 | Na+ |
| Ca(20) | 2,8,8,2 | Ca → Ca2+ + 2e–……………….. Reaction 2 | Ca2+ |
| Cl(17) | 2,8,7 | Cl + e–→ Cl– ………………….……. Reaction 3 | Cl– |
| O(8) | 2,6 | O + 2e–→ O2-…………………… Reaction 4 | O2- |
- Now when Na reacts with Cl, reaction 1 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be NaCl.
- When Na reacts with O, reaction 1 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be Na2
- When Ca reacts with Cl, reaction 2 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaCl2.
- When Ca reacts with O, reaction 2 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaO.
Ionic Vs Covalent Bond:
| Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond |
| The ionic bond is the attraction between positive and negative ions in a crystal and compounds held together by ionic bonds are called ionic compounds. | The covalent bond is a bond formed when two atoms share one or more electron pairs. Each atom contributes an equal number of electrons towards the bond formation. |
| If the difference of ionization potential between the two atoms is more ionic compounds are formed. | Atoms with higher ionization potential are unable to lose their valence electrons and hence prefer to form covalent bonds by sharing of electrons. |
| Atoms with greater electronegativity difference lead to the formation of an ionic bond. | If the electronegativities of the combining atoms do not differ much then the bond formed between them is likely to be covalent. |
| Example: NaCl | Example: HC |
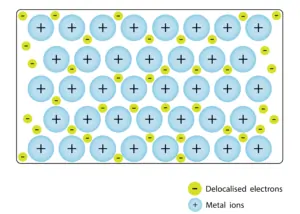
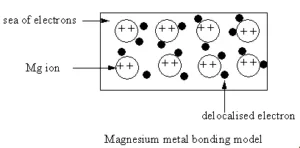
Metallic Bonding
- Metallic bonds connect metal atoms by sharing free electrons in an ‘electron sea’ around cations.
- Delocalized electrons in metallic bonds make metals good conductors of electricity and heat.
- Metals are ductile and malleable because metallic bonding allows atoms to slide and reform bonds.
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. In contrast, covalent and ionic bonds form between two discrete atoms. Metallic bonding is the main type of chemical bond that forms between metal atoms.
Metallic bonds are seen in pure metals and alloys and some metalloids. For example, graphene (an allotrope of carbon) exhibits two-dimensional metallic bonding. Metals, even pure ones, can form other types of chemical bonds between their atoms. For example, the mercurous ion (Hg22+) can form metal-metal covalent bonds. Pure gallium forms covalent bonds between pairs of atoms that are linked by metallic bonds to surrounding pairs.
Process of Bond Formation
- Loss of Valence Electrons: Metal atoms, characteristically having few electrons in their outer shell, tend to lose these electrons easily.
- Formation of Positive Metal Ions: As a result, metal atoms become positively charged ions, while their lost electrons become delocalised.
- Attraction Between Ions and Electrons: The positive metal ions are held together by their collective attraction to the sea of delocalised electrons.
Process of Bond Formation Download the file here
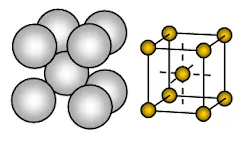
Detailed Structure of the Metallic Lattice
- Close Packing: Metal atoms are packed closely together in a fixed arrangement, which can be either body-centred cubic, face-centred cubic, or hexagonal close-packed.
- Uniform Distribution of Electrons: The delocalised electrons are evenly spread across the lattice, creating a stable structure.
How Metallic Bonds Work
The outer energy levels of metal atoms (the s and p orbitals) overlap. At least one of the valence electrons participating in a metallic bond is not shared with a neighbor atom, nor is it lost to form an ion. Instead, the electrons form what may be termed an “electron sea” in which valence electrons are free to move from one atom to another.
The electron sea model is an oversimplification of metallic bonding. Calculations based on electronic band structure or density functions are more accurate. Metallic bonding may be seen as a consequence of a material having many more delocalized energy states than it has delocalized electrons (electron deficiency), so localized unpaired electrons may become delocalized and mobile. The electrons can change energy states and move throughout a lattice in any direction.
Bonding can also take the form of metallic cluster formation, in which delocalized electrons flow around localized cores. Bond formation depends heavily on conditions. For example, hydrogen is a metal under high pressure. As pressure is reduced, bonding changes from metallic to nonpolar covalent.
Properties Attributed by Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonds impart several important properties to metals that make them commercially desirable. Some of these properties are briefly described in this subsection.
1. Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to allow a charge to move through it. Since the movement of electrons is not restricted in the electron sea, any electric current passed through the metal passes through it, as illustrated below.
When a potential difference is introduced to the metal, the delocalized electrons start moving towards the positive charge. This is the reason why metals are generally good conductors of electric current.
2. Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct/transfer heat. When one end of a metallic substance is heated, the kinetic energy of the electrons in that area increases. These electrons transfer their kinetic energies to other electrons in the sea via collisions.
The greater the mobility of the electrons, the quicker the transfer of kinetic energy. Due to metallic bonds, the delocalized electrons are highly mobile, and they transfer the heat through the metallic substance by colliding with other electrons.
3. Malleability and Ductility
When an ionic crystal (such as sodium chloride crystal) is beaten with a hammer, it shatters into many smaller pieces. This is because the atoms in the crystals are held together in a rigid lattice that is not easily deformed. The introduction of a force (from the hammer) causes the crystal structure to fracture, resulting in the shattering of the crystal.
In the case of metals, the sea of electrons in the metallic bond enables the deformation of the lattice. Therefore, when metals are beaten with a hammer, the rigid lattice is deformed and not fractured. This is why metals can be beaten into thin sheets. Since these lattices do not fracture easily, metals are said to be highly ductile.
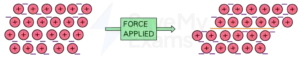
When a force is applied, the layers of positive ions slide over each other
- Most metals are ductile
- This means they can be pulled into wires
- This is also because the atoms are arranged in layers which can slide over each when force is applied
4. Metallic Luster
When light is incident on a metallic surface, the energy of the photon is absorbed by the sea of electrons that constitute the metallic bond. The absorption of energy excites the electrons, increasing their energy levels. These excited electrons quickly return to their ground states, emitting light in the process. This emission of light due to the de-excitation of electrons attributes a shiny metallic lustre to the metal.

Gold has a metallic luster, shiny on a clean face and dull on a worn face like this nugget.
5. High Melting and Boiling Points
As a result of powerful metallic bonding, the attractive force between the metal atoms is quite strong. In order to overcome this force of attraction, a great deal of energy is required. This is the reason why metals tend to have high melting and boiling points. The exceptions to this include zinc, cadmium, and mercury (explained by their electron configurations, which end with ns2).
The metallic bond can retain its strength even when the metal is in its melt state. For example, gallium melts at 29.76oC but boils only at 2400oC. Therefore, molten gallium is a non volatile liquid.
Metallic bonding in sodium
Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Even a metal like sodium (melting point 97.8°C) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the Periodic Table.
Sodium has the electronic structure 1s22s22p63s1. When sodium atoms come together, the electron in the 3s atomic orbital of one sodium atom shares space with the corresponding electron on a neighbouring atom to form a molecular orbital – in much the same sort of way that a covalent bond is formed.
The difference, however, is that each sodium atom is being touched by eight other sodium atoms – and the sharing occurs between the central atom and the 3s orbitals on all of the eight other atoms. And each of these eight is in turn being touched by eight sodium atoms, which in turn are touched by eight atoms – and so on and so on, until you have taken in all the atoms in that lump of sodium.
All of the 3s orbitals on all of the atoms overlap to give a vast number of molecular orbitals which extend over the whole piece of metal. There have to be huge numbers of molecular orbitals, of course, because any orbital can only hold two electrons.
The outer electrons have become delocalised over the whole metal structure. This means that they are no longer attached to a particular atom or pair of atoms, but can be thought of as moving freely around in the whole structure.
So each atom’s outer electrons are involved in this delocalisation or sea of electrons. The rest of each atom (the nucleus and the inner electrons) is essentially a sodium ion, Na+.
Metallic bonding is often described as an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons.
The metal is held together by the strong forces of attraction between the delocalised electrons and the positive ions.
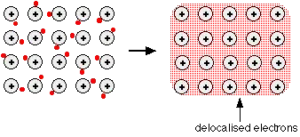
Beware if you are going to use the term “an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons”!
Is a metal made up of atoms or ions? It is made of atoms.
Each positive centre in the diagram represents all the rest of the atom apart from the outer electron, but that electron hasn’t been lost – it may no longer have an attachment to a particular atom, but it’s still there in the structure. Sodium metal is therefore written as Na – not Na+.
Metallic bonding in magnesium
If you work through the same argument with magnesium, you end up with stronger bonds and so a higher melting point.
Magnesium has the outer electronic structure 3s2. Both of these electrons become delocalised, so the “sea” has twice the electron density as it does in sodium. The remaining “ions” also have twice the charge and so there will be more attraction between “ions” and “sea”.
More realistically, each magnesium atom has 12 protons in the nucleus compared with sodium’s 11. In both cases, the nucleus is screened from the delocalised electrons by the same number of inner electrons – the 10 electrons in the 1s2 2s2 2p6 orbitals.
That means that there will be a net pull from the magnesium nucleus of 2+, but only 1+ from the sodium nucleus.
So not only will there be a greater number of delocalised electrons in magnesium, but there will also be a greater attraction for them by the net pull from the magnesium nuclei.
Magnesium atoms also have a slightly smaller radius than sodium atoms, and so the delocalised electrons are closer to the nuclei. Each magnesium atom also has twelve near neighbours rather than sodium’s eight. Both of these factors increase the strength of the bond still further.
Metallic bonding in transition elements
Transition metals tend to have particularly high melting points and boiling points. The reason is that they can involve the 3d electrons in the delocalisation as well as the 4s. The more electrons you can involve, the stronger the attractions tend to be.
Hydrogen Bonding
A hydrogen bond is a type of attractive (dipole-dipole) interaction between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom bonded to another electronegative atom. This bond always involves a hydrogen atom. Hydrogen bonds can occur between molecules or within parts of a single molecule.
Hydrogen bonds are a specific type of intermolecular force.
Hydrogen bonds exist between molecules that have an N-H, O-H or F-H bond
Hydrogen bonding describes a type of permanent dipole-dipole, intermolecular force.
Nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine are highly electronegative elements whereas hydrogen has a very low electronegativity (see Electronegativity). When a hydrogen atom covalently bonds with a nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atom, the bond formed is highly polar.

This high polarity gives rise to permanent dipole-dipole forces between partially negative nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atoms from one molecule and partially positive hydrogen atoms from a neighbouring molecule. These forces are called hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds only occur between molecules that contain nitrogen-hydrogen (N-H), oxygen-hydrogen (O-H) or fluorine-hydrogen (F-H) bonds.
How do hydrogen bonds form?
A hydrogen atom is made up of just one electron and one proton.
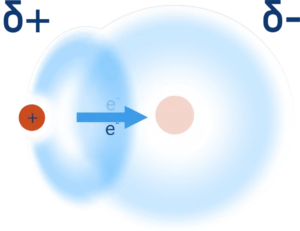
When a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a very electronegative element (such as nitrogen, oxygen or flourine), its electron is pulled away from it and towards the more electronegative element.
This not only creates a polar bond and leaves the hydrogen with a partial positive charge (δ+) but it also leaves the nucleus (proton) of the hydrogen atom ‘exposed’ on one side.
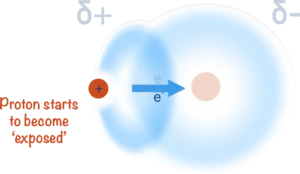
any further electrons around the nucleus of the hydrogen atom. This means as the bonded electron gets pulled away from it, one side of the atom has no electrons around it and this exposes the single proton in the nucleus.
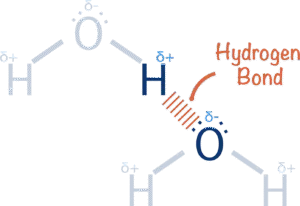
A lone pair of electrons from a nitrogen, oxygen or flourine atom from a similiar bond from a neighbouring molecule will be attracted to this partially exposed proton – giving rise to a ‘hydrogen bond‘.
Examples of Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are found in nucleic acids between base pairs and between water molecules. Hydrogen bonds also form between hydrogen and carbon atoms of different chloroform molecules, between hydrogen and nitrogen atoms of neighboring ammonia molecules, between repeating subunits in the polymer nylon, and between hydrogen and oxygen in acetylacetone. Many organic molecules are subject to hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bond:
- Help bind transcription factors to DNA
- Aid antigen-antibody binding
- Organize polypeptides into secondary structures, such as alpha helix and beta sheet
- Hold together the two strands of DNA
- Bind transcription factors to each other
Hydrogen Bonding in Alcohols and Carboxylic Acid
Alcohol is a type of organic molecule which contains an -OH group. Normally, if any molecule which contains the hydrogen atom is connected to either oxygen or nitrogen directly, then hydrogen bonding is easily formed.
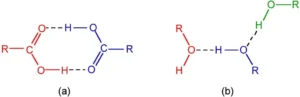
Hydrogen Bonding in Polymers
Hydrogen bonding is an important factor in determining the 3D structures and properties that are acquired by synthetic and natural proteins. Hydrogen bonds also play an important role in defining the structure of cellulose as well as derived polymers such as cotton or flax.
Strength of the Hydrogen Bond
The hydrogen bond is a weak bond. The strength of the hydrogen bond is in-between the weak Van der Waals forces and the strong covalent bonds.
The dissociation energy of the hydrogen bond depends upon the attraction of the shared pair of electrons, and hence on the electronegativity of the atom
Properties of Hydrogen Bonding
- Solubility: Lower alcohols are soluble in water because of the hydrogen bonding which can take place between water and alcohol molecules.
- Volatility: As the compounds involving hydrogen bonding between different molecules have a higher boiling point, they are less volatile.
- Viscosity and surface tension: The substances which contain hydrogen bonding exist as associated molecules. So, their flow becomes comparatively difficult. They have higher viscosity and high surface tension.
- The lower density of ice than water: In the case of solid ice, hydrogen bonding gives rise to a cage-like structure of water molecules. As a matter of fact, each water molecule is linked tetrahedral to four water molecules. The molecules are not as closely packed as they are in a liquid state. When ice melts, this case-like structure collapses, and the molecules come closer to each other. Thus for the same mass of water, the volume decreases and density increases. Therefore, ice has a lower density than water at 273 K. That is why ice floats.
Types of Hydrogen Bonding
There are two types of H bonds, and it is classified as the following:
- Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
- Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
When hydrogen bonding takes place between different molecules of the same or different compounds, it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
For example, hydrogen bonding in water, alcohol, ammonia etc.
Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
The hydrogen bonding which takes place within a molecule itself is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
It takes place in compounds containing two groups such that one group contains a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom, and the other group contains a highly electronegative atom linked to a lesser electronegative atom of the other group.
The bond is formed between the hydrogen atoms of one group with the more electronegative atom of the other group.
Problem: Indicate which of the following molecules could form hydrogen bonds with other like molecules.
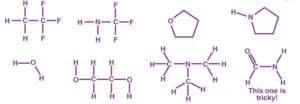
Symmetric Hydrogen Bond
This is a special type of hydrogen bond where the proton is usually placed in the middle between two identical atoms. The strength of the bond between each atom is equal. The symmetric hydrogen bond is a type of three-centre four-electron bond. This bond is also much stronger compared to the “normal” hydrogen bond, and its strength is almost similar to a covalent bond.