Nomenlcature Of Alkanes
Naming alkenes( Nomenclature of alkenes) is done by replacing ending -ane of alkanes by -ene. Like, ethane becomes ethene and soon. International union of Pure and Applied Chemistry devised a rule for naming organic compounds through which each compound has given a specific name and with the help of this rule we can easily recognize a compound in billions or trillions of compounds. In case of naming geometrical isomers , E-Z nomenclature is used.
There are generally, two systems for naming alkenes similar to Alkanes;
- Trivial system(common names)
- IUPAC System
- E-Z Nomenclature( for geometric isomers)
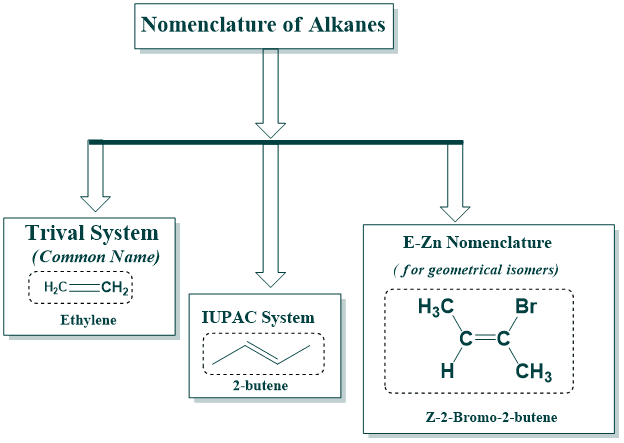
Trivial system of naming alkenes:
In this system, alkenes are named by replacing the –ane of Alkanes containing same no. of carbon atoms by -ylene. For example;
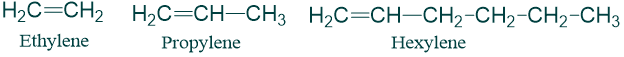
A few interesting trivial names are also common in use:

IUPAC System of naming alkenes:
This system is more versatile and can be used for substances having more than one double bond. According to this system alkenes are generally named by replacing -ane of Alkanes by -ene. For example, “Ethane” changes to “Ethene” , “Propane” changes to “Propene“, “Butane” changes to “Butene” and soon. Except ethene and propene higher alkenes exists in more than one isomeric forms.
Rules for naming alkenes:
The rules for naming alkenes are similar to those of Alkanes which are discussed below;
- The longest continuous Carbon chain containing both carbon atoms of double bond is selected as parent chain which is named by replacing -ane of Alkanes by ending -ene. For example
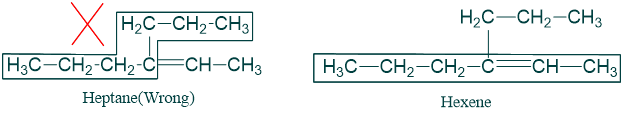
2) The carbon atoms of parent chain are numbered in such a way that double bonded carbon atom gets lowest possible number.
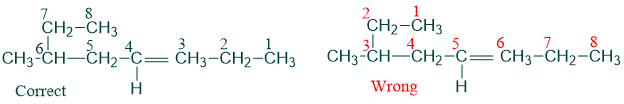
3) If any alkyl substituent is present then it is written before the name of parent chain with its assigned number placed before it. In this case double bond is still given preference in numbering.
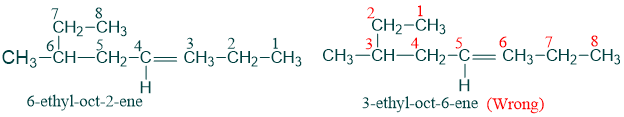
4) If there are more than one double bonds present in parent chain then we use the suffixes dienes, trienes etc. to show the presence of 2,3 double bonds respectively.
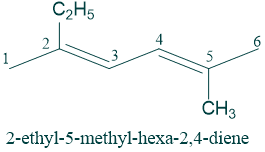
5) In case of cycloalkenes, numbering is always starting from one of the double-bonded carbon atom such that when we continue toward other carbon of double bond , the substituent gets lowest possible number.
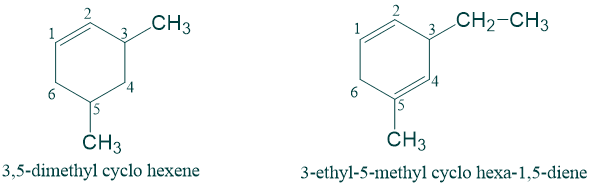
6) There are few alkenyl groups for which we use common names preferentially as compared to their IUPAC names.
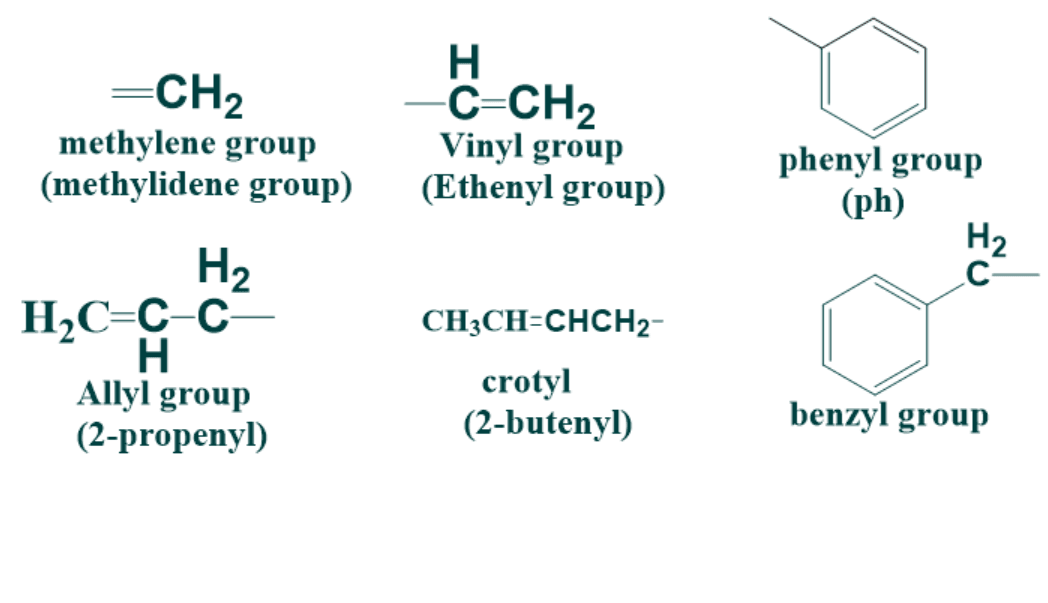
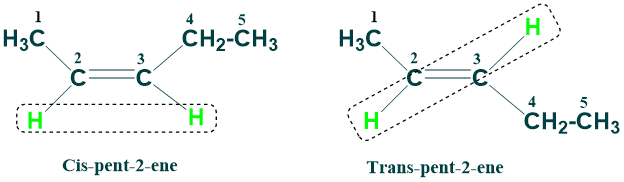
Cis-Trans Nomenclature:
Restricted rotation of C-C double bond gives rise to new type of isomerism called cis – trans or geometric isomerism.
This system of nomenclature works best for alkenes in which both double-bonded carbons have same set of substituents. If similar groups are present on same side of double bond then cis prefix is used ,if different groups are present on same side the prefix trans is used. Examples of cis trans isomers of alkenes are given below:
But this system of naming alkenes failed if four different groups are present on double bonded carbon atoms similar to chiral carbon.
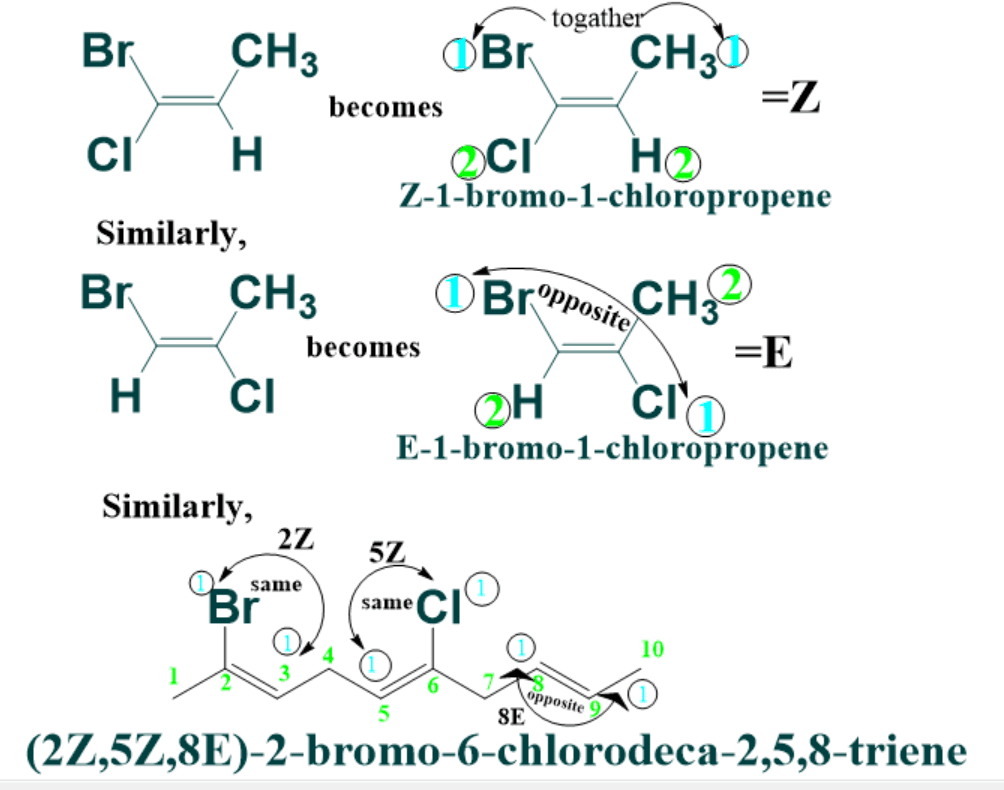
What is E and Z Nomenclature of Alkenes:
The cis trans nomenclature for geometric isomers fails in naming of compound having four different groups .
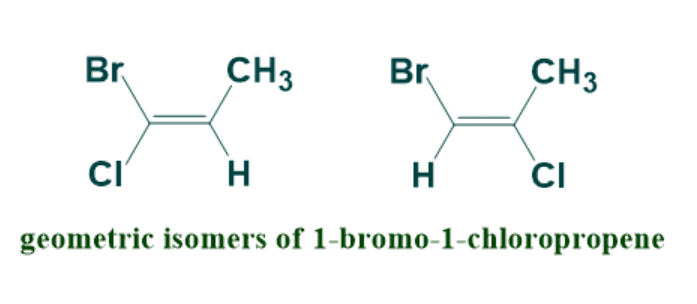
To solve this problem, E-Z nomenclature was introduced which is based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention rules.
According to this system the two groups on each double bonded carbon are ranked in order of priority. The priority of groups decided on the basis of their atomic masses. Higher atomic masses elements are preferred over lower.
If both the groups of higher priority are on same side of double bond the geometric isomer is designated as Z ( from German word zuzammen meaning “together”).
If higher priority groups are present on opposite side then geometric isomer is designated as E ( from entgegen meaning “across”).